Types of Cell Signaling definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (10)
Cell Signaling
The process by which cells communicate with each other to coordinate functions and maintain homeostasis either through direct contact or by releasing signaling molecules that affect distant cells.
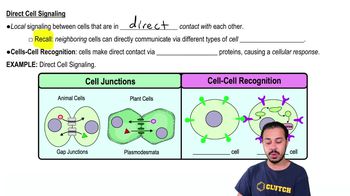
Cell Junctions
Structures that connect adjacent cells, facilitating direct communication and exchange of materials, such as ions and signaling molecules, to maintain homeostasis in multicellular organisms.
Gap Junctions
Protein channels connecting the cytoplasm of adjacent animal cells, allowing direct exchange of ions, nutrients, and signaling molecules for cell communication.
Plasmodesmata
Channels connecting plant cells' cytoplasm, allowing direct exchange of nutrients, materials, and signaling molecules for communication.
Cell To Cell Recognition
When cells recognize and bind to each other via specific membrane proteins, triggering a cellular response.
Membrane Proteins
Proteins embedded in the cell membrane that facilitate cell signaling, transport, and recognition by interacting with other cells or molecules.
Cellular Response
The process by which a cell reacts to a signal, leading to a specific change in cellular activity or function.
Synaptic Signaling
A nerve cell releases neurotransmitters across a synapse to a target cell, enabling rapid, localized communication.
Synapse
A junction between two nerve cells where neurotransmitters are released to transmit signals to the next cell, enabling communication within the nervous system.
Paracrine Signaling
Local cell signaling where a cell releases signaling molecules that affect nearby target cells within the same tissue, without entering the bloodstream.