Steps to DNA Cloning definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (20)
DNA Cloning
The process of creating identical copies of a DNA sequence by inserting it into a host organism, typically involving the creation of recombinant DNA and its transformation into bacteria.
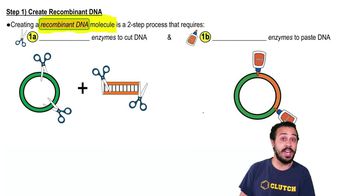
Recombinant DNA
A DNA molecule formed by combining DNA from two different sources, often using restriction enzymes and DNA ligase, to create a new genetic sequence.
Bacterial Plasmid
A small, circular DNA molecule in bacteria, separate from chromosomal DNA, often used in genetic engineering to replicate and express foreign genes.
Gene Of Interest
A specific gene that is targeted for study or manipulation, often inserted into a vector for cloning or expression in a host organism.
Protein X
A protein produced by bacteria after the insertion of a recombinant DNA molecule containing a gene of interest from another species.
Restriction Enzymes
Enzymes that recognize specific DNA sequences and cut the DNA at these sites, creating sticky ends that can be joined with complementary DNA fragments.
DNA Ligases
Enzymes that join DNA fragments by forming phosphodiester bonds, essential for DNA replication, repair, and recombinant DNA technology.
Cloning Vector
A DNA molecule used to transport foreign genetic material into another cell, where it can be replicated and/or expressed.
Transformation
The process by which bacteria uptake external recombinant DNA, allowing them to express new genetic information.
Sticky Ends
Single-stranded overhangs of DNA created by restriction enzymes that can anneal with complementary sequences, facilitating the joining of different DNA fragments.
Restriction Site
A specific DNA sequence recognized and cut by a restriction enzyme, creating sticky or blunt ends for recombination.
Endonucleases
Enzymes that cleave DNA at specific internal sites, creating fragments with sticky or blunt ends, facilitating genetic recombination.
DNA Polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to a pre-existing strand during DNA replication.
Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between the nucleotide base pairs, essential for DNA replication and repair processes.
Primase
An enzyme that synthesizes short RNA primers to provide a starting point for DNA polymerase during DNA replication.
Transgenic Organisms
An organism with DNA from another species integrated into its genome, enabling it to express foreign genes.
Hybrid Organisms
Organisms created by mating two different species, resulting in offspring with traits from both parent species.
Polyploid Organisms
Organisms with more than two complete sets of chromosomes, often resulting in increased size and vigor, commonly found in plants.
Genome
The complete set of an organism's DNA, including all of its genes and non-coding sequences, that contains the instructions for building and maintaining that organism.
Hydrogen Bond
A weak bond formed between a hydrogen atom in one molecule and an electronegative atom (like oxygen or nitrogen) in another, crucial for the structure of DNA and proteins.