Putting it All Together exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (29)
Hardy-Weinberg principle
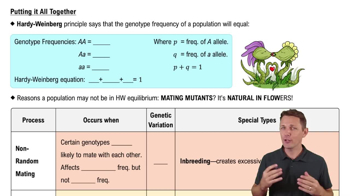
Predicts genotype frequencies in a population using the equation p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1.
What does p represent in the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
The frequency of the dominant allele in the population.
What does q represent in the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
The frequency of the recessive allele in the population.
p + q = 1
The sum of the frequencies of the dominant and recessive alleles in a population.
Non-random mating
Occurs when certain genotypes are more likely to mate with each other, affecting genotype frequency but not allele frequency.
What is inbreeding?
A type of non-random mating that increases homozygosity and can lead to inbreeding depression.
Mutation
Random changes in DNA that create new alleles, increasing genetic variation.
Natural selection
Process where certain alleles become more common because they enhance survival and reproduction.
Genetic drift
Random changes in allele frequencies due to chance events, more significant in small populations.
Gene flow
Movement of alleles between populations, increasing genetic variation and reducing differences between populations.
What is the founder effect?
When a new population is started by a small number of individuals, leading to reduced genetic diversity.
Population bottleneck
A sudden reduction in population size that increases the rate of genetic drift.
Directional selection
Natural selection that favors one extreme phenotype, causing a shift in the population's average phenotype.
Stabilizing selection
Natural selection that favors the average phenotype, reducing variation without changing the average.
Disruptive selection
Natural selection that favors both extreme phenotypes, potentially leading to multiple distinct phenotypes.
Balancing selection
Maintains multiple alleles in a population, increasing genetic variation.
Frequency-dependent selection
A type of balancing selection where the fitness of a phenotype depends on its frequency relative to other phenotypes.
Heterozygote advantage
A type of balancing selection where heterozygotes have higher fitness than either homozygote.
What is the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A state where allele and genotype frequencies remain constant in a population from generation to generation.
What are the assumptions of the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
Random mating, no mutation, no natural selection, large population size, and no gene flow.
What is genetic variation?
The diversity of alleles and genotypes within a population.
How does natural selection affect genetic variation?
Generally decreases genetic variation by favoring certain alleles over others.
How does genetic drift affect genetic variation?
Reduces genetic variation as alleles are lost from the population.
How does gene flow affect genetic variation?
Increases genetic variation by introducing new alleles into a population.
Point mutation
A change to a single nucleotide in DNA.
Duplication
A type of mutation where a section of a chromosome is repeated, potentially creating new genes.
Horizontal gene transfer
The movement of genes between different species, not through parent-offspring inheritance.
What is inbreeding depression?
Reduced fitness in a population due to the pairing of deleterious recessive alleles through inbreeding.
What is the effect of a population bottleneck on genetic drift?
Increases the rate of genetic drift due to a sudden reduction in population size.