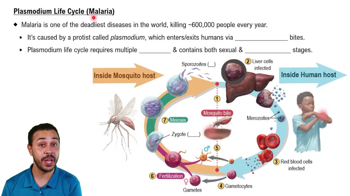
Protist Life Cycles exam Flashcards
 Back
BackProtist Life Cycles exam
1/27
Terms in this set (27)
- Alternation of generationsA life cycle involving both haploid (gametophyte) and diploid (sporophyte) stages, each with multicellular components.
- What is the haploid multicellular stage in alternation of generations called?Gametophyte
- SporophyteThe diploid multicellular stage in alternation of generations that undergoes meiosis to produce spores.
- What do gametophytes produce?Gametes
- HeteromorphicWhen the sporophyte and gametophyte stages are structurally different.
- IsomorphicWhen the sporophyte and gametophyte stages look the same.
- What is the only diploid stage in a haploid-dominant life cycle?Zygote
- What process does the zygote undergo in a haploid-dominant life cycle?Meiosis
- Diploid-dominant life cycleA life cycle where the only haploid cells are the gametes.
- In a diploid-dominant life cycle, what do mature cells undergo to form gametes?Meiosis
- What is the role of spores in alternation of generations?Spores are units of asexual reproduction that are generally haploid and unicellular.
- What happens after gametes fuse in alternation of generations?Fertilization occurs, forming a zygote.
- What does the zygote form after undergoing mitosis in alternation of generations?Sporophyte
- What is the main difference between haploid-dominant and diploid-dominant life cycles?In haploid-dominant, the zygote undergoes meiosis directly; in diploid-dominant, the zygote undergoes mitosis to form the organism.
- What type of organisms can have haploid-dominant life cycles?Unicellular or multicellular organisms
- What is the process by which haploid cells reproduce asexually in haploid-dominant life cycles?Mitosis and cell division
- What is the only haploid part of a diploid-dominant organism's life cycle?Gametes
- What is the significance of understanding eukaryotic life cycles?It is crucial for grasping reproductive strategies in various organisms, including plants and protists.
- What happens to the zygote in a diploid-dominant life cycle?It undergoes mitosis to form the organism.
- What is the process by which gametophytes form from spores?Mitosis
- What is the main reproductive strategy in haploid-dominant life cycles?Asexual reproduction through mitosis and cell division
- What is the role of meiosis in diploid-dominant life cycles?To form gametes from mature cells
- What is the outcome of fertilization in alternation of generations?Formation of a zygote
- What is the structural difference between heteromorphic and isomorphic organisms?Heteromorphic organisms have different forms for sporophyte and gametophyte stages, while isomorphic organisms have the same form for both stages.
- What is the primary characteristic of a diploid-dominant life cycle?The organism is primarily diploid, with gametes being the only haploid cells.
- What is the primary characteristic of a haploid-dominant life cycle?The organism is primarily haploid, with the zygote being the only diploid stage.
- What is the process by which gametes are formed in haploid-dominant life cycles?Mitosis