Population Ecology quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackPopulation Ecology quiz
1/17
Terms in this set (17)
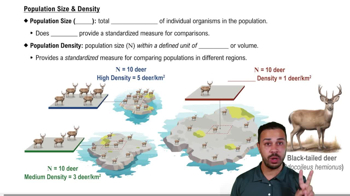
- What is the definition of a population in population ecology?A population is all the organisms of the same species that inhabit a certain area.
- What does population density measure?Population density measures the number of individuals per area or volume.
- What are biotic factors in population ecology?Biotic factors are living components like other organisms that can act as food or competitors.
- What are abiotic factors in population ecology?Abiotic factors are non-living components like climate and physical barriers such as mountain ranges or bodies of water.
- What is the difference between immigration and emigration?Immigration is the influx of new individuals from another population, while emigration is the movement of individuals away from a population.
- What is a metapopulation?A metapopulation consists of populations that are separated by space but interact in some way.
- What is the mark-recapture method used for?The mark-recapture method is used to estimate population size by capturing, marking, and recapturing organisms.
- What is demography in the context of population ecology?Demography is the statistical study of populations and how they change over time.
- What is a survivorship curve?A survivorship curve is a graphical representation of the number of individuals of a specific species that survive to each age.
- What does the term 'fecundity' refer to?Fecundity refers to the reproductive rate of an organism in a population.
- What is the carrying capacity (K) in population ecology?Carrying capacity is the maximum population size that an area can sustain due to limited resources.
- What is the difference between exponential growth and logistic growth?Exponential growth is a J-shaped curve showing rapid population increase, while logistic growth is an S-shaped curve showing population growth that levels off at carrying capacity.
- What is the ecological footprint?The ecological footprint is the amount of land needed to sustain an organism or a population's use of resources.
- What is the replacement rate in demography?The replacement rate is the fertility rate required for women to give birth to enough children to sustain the population.
- What are density-dependent factors?Density-dependent factors change growth rates based on population density, such as competition, disease, and predation.
- what is most likely to happen to a population of mice that becomes isolated on an island?When a population of mice becomes isolated on an island, it is likely to experience changes in population size due to the limited space and resources. The population may initially grow if resources are abundant, but over time, factors such as limited resources, lack of genetic diversity, and environmental changes could lead to fluctuations in population size. Additionally, the isolated population may develop unique traits due to genetic drift and natural selection.
- which three statements may correctly explain why the population size increases after time point c?1. Increased Birth Rate: A higher birth rate could lead to an increase in population size if more individuals are being born than are dying. 2. Immigration: An influx of individuals from other areas could contribute to population growth by adding new members to the population. 3. Decreased Death Rate: A reduction in the death rate, possibly due to improved living conditions or fewer predators, could result in a net increase in population size.