Population Ecology definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (11)
Population
A group of individuals of the same species living in a specific area, interacting and interbreeding, with dynamics influenced by births, deaths, immigration, and emigration.
Abundance
The number of individuals of a species in a given area, reflecting population size and density, crucial for understanding ecosystem dynamics and resource allocation.
Distribution
The spatial arrangement of individuals within a population, influenced by factors like resource availability, social interactions, and environmental conditions.
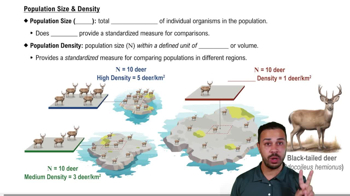
Population Density
The number of individuals of a species per unit area or volume, indicating how crowded a population is within its habitat.
Range
The geographic area where a species is found, influenced by biotic and abiotic factors such as climate, food availability, and physical barriers.
Abiotic factors
Non-living environmental components like climate, water, soil, and physical barriers that influence the distribution and abundance of organisms in an ecosystem.
Population Dynamics
Study of how population size, age structure, and distribution change over time due to births, deaths, immigration, and emigration, influenced by biotic and abiotic factors.
Dispersion
The spatial arrangement of individuals within a population, influenced by factors like resource availability, social interactions, and competition, resulting in patterns such as random, clumped, or uniform.
Demography
The statistical study of populations, focusing on size, structure, distribution, and changes over time due to births, deaths, immigration, and emigration.
Generation
The average time between a mother's first offspring and her daughter's first offspring, indicating the turnover rate of generations in a population.
Life Table
A statistical tool that summarizes the survival and reproductive rates of individuals in a population, often segmented by age, to predict life expectancy and mortality rates.