Phylogeny definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (13)
Taxonomy
The science of defining, categorizing, and classifying organisms based on shared characteristics and genetic relatedness.
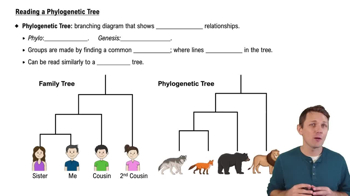
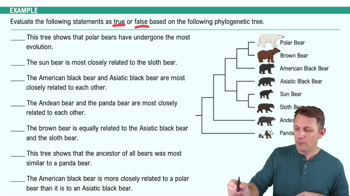
Phylogeny
The study of the evolutionary relationships among species, often depicted as a branching diagram called a phylogenetic tree, showing inferred connections based on genetic, morphological, or other data.
Genus
A taxonomic rank grouping species that share common characteristics and are closely related, positioned above species and below family in the hierarchy.
Species
A group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring, sharing common characteristics and genetic heritage, and distinct from other groups in terms of reproductive isolation.
Domains
Domains are the highest taxonomic rank, categorizing life into three broad groups based on cell type: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. They represent the most inclusive classification, encompassing all known organisms.
Kingdoms
Kingdoms are major taxonomic groups within domains, categorizing organisms based on fundamental traits and evolutionary relationships, such as cell structure, metabolism, and genetic similarities.
Phylum
A taxonomic rank below kingdom, grouping organisms based on major body plans and shared characteristics, reflecting evolutionary relationships.
Class
A taxonomic rank grouping organisms that share a common ancestor and exhibit similar characteristics, positioned below phylum and above order in the hierarchy.
Order
A taxonomic rank used to classify organisms, grouping families that share common characteristics and evolutionary traits, situated between class and family in the hierarchy.
Family
A taxonomic rank grouping related organisms that share a common ancestor, situated between order and genus, used to classify organisms based on evolutionary relationships.
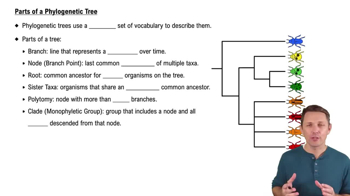
Cladistics
A method of classifying organisms based on common ancestry and evolutionary relationships, using shared characteristics to form groups called clades.
Homology
Similarity between organisms due to shared ancestry, indicating common evolutionary origins.
Analogy
Similarity between organisms due to convergent evolution, not shared ancestry, often resulting from adaptation to similar environments.