Overview of Animals definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (15)
Zygote
A fertilized egg cell formed by the union of a sperm and an egg, which undergoes rapid cell divisions to develop into a multicellular organism.
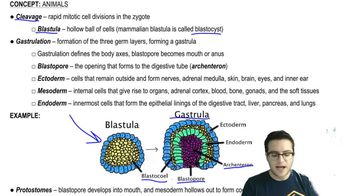
Cleavage
A series of rapid mitotic divisions in early embryonic development, resulting in a multicellular structure without an increase in overall size, leading to the formation of a blastula.
Blastula
A hollow sphere of cells formed during early embryonic development, resulting from rapid mitotic divisions of a zygote.
Gastrulation
The process in early embryonic development where a blastula reorganizes into a gastrula, forming three primary germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, which will develop into all tissues and organs.
Germ Layers
Layers of cells in an embryo that differentiate into specific tissues and organs, forming the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm in triploblastic organisms.
Ectoderm
The outermost germ layer in an embryo, forming structures such as the skin, brain, eyes, and nerves.
Endoderm
The innermost germ layer in animal embryos, forming the lining of the digestive tract, liver, pancreas, and lungs.
Mesoderm
The middle germ layer in an embryo that forms muscles, bones, blood, and connective tissues.
Protostome
An organism whose blastopore develops into the mouth during early embryonic development, characterized by spiral and determinate cleavage.
Deuterostome
An organism whose blastopore develops into the anus, with the mouth forming secondarily, and typically exhibits radial and indeterminate cleavage during embryonic development.
Coelom
A body cavity derived entirely from the mesoderm, surrounding the digestive tract, and found only in triploblastic organisms.
Radial Symmetry
A body plan where body parts are arranged around a central axis, allowing multiple planes to divide the organism into roughly identical halves.
Bilateral Symmetry
A body plan where an organism can be divided into two mirror-image halves along a single plane, typically resulting in distinct left and right sides.
Notochord
A flexible, rod-like structure in embryonic development that provides support and signals for the formation of the neural tube and vertebral column in chordates.
Neural Tube
A hollow structure formed from the ectoderm folding inwards, which later differentiates into the brain and spinal cord during embryonic development.