Osmoregulation and Excretion quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (16)
What is osmoregulation?
Osmoregulation is the homeostatic mechanism that allows organisms to balance their solute concentration and deal with water loss.
What is the primary function of the excretory system?
The primary function of the excretory system is to eliminate waste from the body, which involves the loss of solutes and water.
What is the main organ involved in the excretory system?
The main organ involved in the excretory system is the kidney, which filters blood plasma and forms urine.
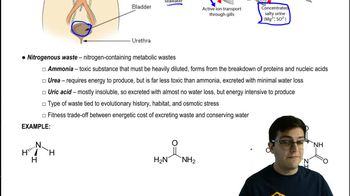
How is ammonia formed in the body?
Ammonia is formed from the breakdown of proteins and nucleic acids, which contain nitrogen in their structures.
Why is ammonia considered toxic in the body?
Ammonia is toxic because it needs to be heavily diluted to be safe in the body.
What is the difference between urea and ammonia in terms of water usage?
Urea is less toxic than ammonia and can be excreted with minimal water loss, making it suitable for organisms with limited water availability.
What is the advantage of excreting uric acid for desert-dwelling organisms?
Uric acid is almost insoluble and can be excreted with minimal water loss, which is crucial for organisms in dry climates.
What is the role of the nephron in the kidney?
The nephron filters blood, reabsorbs valuable solutes and water, and secretes waste products to form urine.
What is the function of the loop of Henle in the nephron?
The loop of Henle reabsorbs water and salt and helps maintain the osmotic gradients necessary for kidney function.
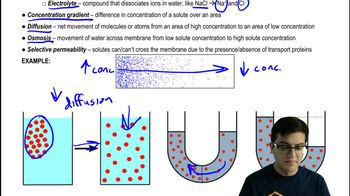
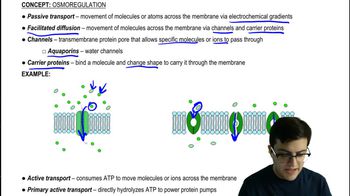
What is the significance of selective permeability in osmosis?
Selective permeability allows certain solutes to cross a membrane while preventing others, facilitating osmosis to balance solute concentrations.
What is the role of aquaporins in the cell membrane?
Aquaporins are water channels that facilitate the efficient passage of water through the cell membrane.
What is the role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in the kidney?
ADH increases the permeability of the distal tubule and collecting duct to water, enhancing water reabsorption and reducing blood osmolarity.
- which would most likely occur in the kidney?In the kidney, key processes such as filtration, selective reabsorption, and secretion occur. Filtration happens in the renal corpuscle, where blood plasma is filtered to form filtrate. Selective reabsorption in the proximal tubule allows valuable solutes and water to be reabsorbed into the blood, while waste products are secreted into the filtrate for excretion.
- which of the following processes must freshwater fish undertake to maintain homeostasis?Freshwater fish must actively excrete excess water and absorb salts to maintain homeostasis. They do this by producing dilute urine and using specialized cells in their gills to uptake ions from the surrounding water, counteracting the osmotic influx of water due to their hypoosmotic environment.
- how does urine osmolarity compare between the two treatment groups?Urine osmolarity can vary between treatment groups based on factors such as hydration status and hormonal regulation. For instance, in a group with high ADH levels, urine osmolarity would be higher due to increased water reabsorption, whereas a group with low ADH levels would have lower urine osmolarity due to less water reabsorption.
- how does the contractile vacuole in a single-celled organism function to maintain homeostasis?The contractile vacuole in single-celled organisms functions to maintain homeostasis by expelling excess water that accumulates inside the cell. This process helps to regulate the cell's internal osmotic pressure, preventing it from bursting in hypotonic environments.