Osmoregulation and Excretion definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (8)
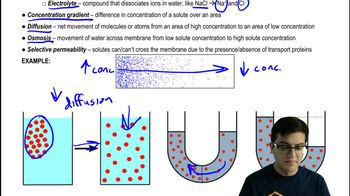
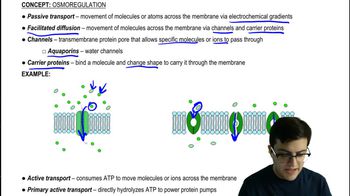
Osmoregulation
The homeostatic process by which organisms regulate their internal solute concentrations and water balance to maintain optimal cellular function.
Excretion
The process of removing metabolic waste products from an organism's body, primarily involving the elimination of nitrogenous wastes, excess salts, and water, to maintain homeostasis.
Bladder
A muscular sac in the excretory system that stores urine produced by the kidneys until it is ready to be expelled from the body through the urethra.
Urethra
A tube that transports urine from the bladder to the external environment, playing a crucial role in the excretory system by facilitating the final step of waste elimination from the body.
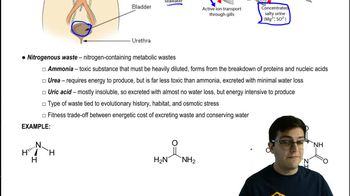
Nitrogenous Waste
Nitrogenous waste is a toxic byproduct of protein and nucleic acid metabolism, primarily excreted as ammonia, urea, or uric acid, depending on an organism's habitat and water availability.
Uric Acid
A nitrogenous waste product excreted by some animals, particularly those in arid environments, that is energy-intensive to produce but conserves water due to its low solubility.
Nephron
A microscopic functional unit of the kidney that filters blood, reabsorbs essential substances, and secretes waste to form urine, maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance.
Filtrate
A solution of water and small solutes, such as salts, sugars, and amino acids, formed after blood plasma is filtered through the kidney's glomerulus into Bowman's capsule.