Nucleic Acids exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (28)
Nucleic Acids
Biomolecules that store and encode genetic information, primarily DNA and RNA.
What are the building blocks of nucleic acids?
Nucleotides.
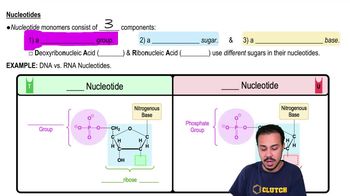
Nucleotide
The monomer of nucleic acids, consisting of a phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
What are the two types of nitrogenous bases?
Pyrimidines and Purines.
Pyrimidines
Single-ringed nitrogenous bases, including cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
Purines
Double-ringed nitrogenous bases, including adenine and guanine.
What is the structure of DNA?
A double helix with antiparallel strands.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, typically single-stranded and involved in protein synthesis.
What type of bond links nucleotides together?
Phosphodiester bonds.
Phosphodiester Bond
A covalent bond that links nucleotides together, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone of nucleic acids.
What are the components of a nucleotide?
A phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
Pentose Sugar
A five-membered ring sugar found in nucleotides; deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA.
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
Ribose has a hydroxyl group at the 2' position, while deoxyribose lacks this oxygen.
Directionality of Nucleic Acids
Indicated by 5' and 3' ends, referring to the orientation of the sugar-phosphate backbone.
What pairs with adenine in DNA?
Thymine.
What pairs with cytosine in DNA?
Guanine.
What nitrogenous base is unique to RNA?
Uracil.
What nitrogenous base is unique to DNA?
Thymine.
Antiparallel Strands
Two strands of DNA that run in opposite directions (5' to 3' and 3' to 5').
What is the primary function of DNA?
To store genetic or hereditary information.
What is the primary function of RNA?
To act as a template for synthesizing proteins.
What is the sugar-phosphate backbone?
The alternating chain of sugar and phosphate to which the DNA and RNA nitrogenous bases are attached.
Base Pairing Rules
Adenine pairs with thymine (or uracil in RNA), and cytosine pairs with guanine.
What is the structure of RNA?
Typically a single-stranded nucleotide chain.
Hydrogen Bonds in DNA
Bonds that form between nitrogenous base pairs, holding the two DNA strands together.
What is the role of phosphodiester bonds in nucleic acids?
They link nucleotides together, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA in terms of structure?
DNA is double-stranded and forms a double helix, while RNA is usually single-stranded.
What is the significance of the 5' and 3' ends in nucleic acids?
They indicate the directionality of the nucleic acid chain.