Back
BackNucleic Acids definitions
Terms in this set (34)
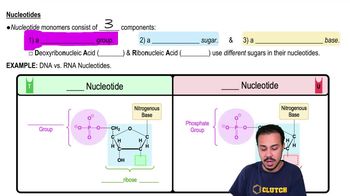
Nucleotides
Monomers of nucleic acids, each consisting of a phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. They form DNA and RNA, differing in their sugar components and some nitrogenous bases.
Nucleic Acids
Macromolecules composed of nucleotide chains, which store and transmit genetic information, and include DNA and RNA, differing mainly in their sugar components and nitrogenous bases.
Monomers
Small molecules that can join together to form larger polymers, serving as the building blocks for complex macromolecules like nucleic acids, proteins, and polysaccharides.
Phosphate Group
A functional group consisting of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms, crucial in forming the backbone of DNA and RNA by linking nucleotides together.
Phosphorus Atom
A central element in nucleotides, crucial for forming the sugar-phosphate backbone in DNA and RNA, enabling the storage and transfer of genetic information.
Pentose Sugar
A five-carbon sugar found in nucleotides, forming part of the backbone of DNA and RNA, differing by the presence or absence of an oxygen atom.
Ring
A closed loop structure found in molecules, such as the pentose sugar in nucleotides, consisting of atoms connected by covalent bonds, often forming a key part of the molecule's backbone.
Nitrogenous Base
A molecule containing nitrogen that forms part of a nucleotide, pairing with a complementary base to help encode genetic information in DNA and RNA.
DNA
A molecule composed of two antiparallel strands forming a double helix, with each strand consisting of nucleotides that include a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group, and nitrogenous bases.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
A molecule composed of two antiparallel strands forming a double helix, with a backbone of deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups, and nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine).
RNA
A molecule that carries genetic information, composed of a ribose sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous bases (adenine, uracil, cytosine, guanine).
Ribose Sugar
A five-carbon sugar with a hydroxyl group on the 2' carbon, essential in the structure of RNA nucleotides.
Deoxyribose Sugar
A five-carbon sugar in DNA, lacking one oxygen atom compared to ribose, crucial for forming the DNA backbone.
Hydroxyl Group
A functional group consisting of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (-OH), commonly found in alcohols and sugars, and plays a key role in the structure of nucleotides.
Hydrogen
A light, colorless element with one proton, essential in forming water and organic compounds, and involved in energy transfer and acid-base balance in biological systems.
Genetic Material
Molecules composed of nucleotides, which include a phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base, forming the basis of heredity and encoding genetic information.
Covalent Bonds
A type of chemical bond where atoms share pairs of electrons to achieve stability, forming molecules with strong, stable connections.
Phosphodiester Bonds
Covalent bonds linking nucleotides in nucleic acids, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone and providing directionality with 5' and 3' ends.
Sugar Phosphate Backbone
A structural framework in DNA and RNA consisting of alternating sugar and phosphate groups, linked by phosphodiester bonds, providing stability and directionality to the nucleic acid strands.
Directionality
The orientation of nucleic acid strands, with one end having a free phosphate group (5') and the other a free hydroxyl group (3'), crucial for processes like replication and transcription.
5 Prime End
The end of a nucleic acid strand with a free phosphate group attached to the fifth carbon of the sugar molecule.
3 Prime End
The end of a nucleic acid strand with a free hydroxyl group attached to the 3' carbon of the sugar molecule.
Cytosine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA, pairs with guanine, and plays a crucial role in encoding genetic information.
Thymine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA, pairs with adenine, and is replaced by uracil in RNA.
Deoxyribonucleotides
Molecules composed of a phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base, forming the building blocks of DNA.
Polymer
A large molecule composed of repeating structural units (monomers) linked by covalent bonds, forming complex structures like DNA, proteins, and synthetic materials.
Dehydration Synthesis
A chemical reaction that joins monomers by removing a water molecule, forming a covalent bond between them.
Antiparallel
Two DNA strands run in opposite directions: one 5' to 3', the other 3' to 5'.
Complimentary Base Pairing
The specific pairing of nitrogenous bases in DNA and RNA, where adenine pairs with thymine (or uracil in RNA) and cytosine pairs with guanine, stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen Bonding
Attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom (like oxygen or nitrogen) and another electronegative atom, crucial for DNA base pairing and protein structure.
Nucleobases
Nitrogenous bases in nucleotides that pair via hydrogen bonds to form the rungs of the DNA double helix or the single-stranded RNA, crucial for genetic encoding and protein synthesis.
Stabilize
To maintain or support the structural integrity of a molecule, often through specific bonds or interactions, ensuring it remains functional and stable.
Chains
Linear sequences of nucleotides linked by phosphodiester bonds, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone of nucleic acids, with directionality from 5' to 3' ends.
Strands
Two long chains of nucleotides in DNA or RNA, running in opposite directions, forming the backbone of the molecule.