Mendel's Experiments exam Flashcards
 Back
BackMendel's Experiments exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
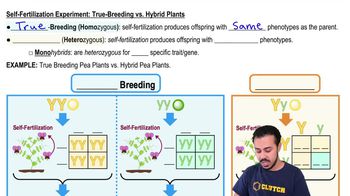
- Self-fertilizationA type of fertilization involving one parent, producing true-breeding offspring with identical phenotypes.
- What is cross-fertilization?A type of fertilization involving two parents, leading to hybrid offspring with varied phenotypes.
- True-breedingOrganisms that, when self-fertilized, produce offspring with the same phenotype as the parent.
- What are hybrids in Mendel's experiments?Plants that, upon self-fertilization, produce offspring with mixed phenotypes.
- Dominant traitA trait that appears in the offspring if at least one parent contributes it.
- What is a recessive trait?A trait that is masked by the presence of a dominant trait and only appears when two recessive alleles are present.
- Punnett squareA diagram used to predict the genotype and phenotype combinations of a genetic cross.
- What is the P generation?The parental generation in Mendel's experiments, the original set of parents.
- F1 generationThe first filial generation, offspring of the P generation.
- What is the F2 generation?The second filial generation, offspring of the F1 generation.
- HomozygousHaving two identical alleles for a particular gene.
- What does heterozygous mean?Having two different alleles for a particular gene.
- MonohybridAn organism that is heterozygous for one specific trait.
- What did Mendel discover about yellow and green pea plants?Yellow is the dominant trait, and green is the recessive trait.
- Self-fertilization in true-breeding plantsProduces offspring with the same phenotype as the parent.
- What happens in cross-fertilization of yellow and green pea plants?All offspring are yellow if the yellow parent is homozygous dominant.
- Heterozygous offspringOffspring with one dominant and one recessive allele.
- What is the significance of the F1 generation in Mendel's experiments?It helps to understand the inheritance of traits from the P generation.
- F2 generation phenotype ratioTypically shows a 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive traits.
- What does a Punnett square show?The possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from a genetic cross.
- Homozygous dominantHaving two dominant alleles for a particular gene.
- What is homozygous recessive?Having two recessive alleles for a particular gene.
- PhenotypeThe observable physical or biochemical characteristics of an organism.
- What is genotype?The genetic constitution of an organism.
- Mendel's use of pea plantsAllowed him to control fertilization and observe inheritance patterns.
- What did Mendel's experiments demonstrate?The principles of inheritance, including dominant and recessive traits.
- Cross-fertilization resultsCan produce a mixture of phenotypes, indicating heterozygosity.
- What is the purpose of categorizing generations (P, F1, F2)?To track inheritance patterns and genetic variation across generations.
- Mendel's discovery of dominant and recessive traitsOccurred through cross-fertilization experiments with yellow and green pea plants.