Logistic Population Growth exam Flashcards
Terms in this set (27)
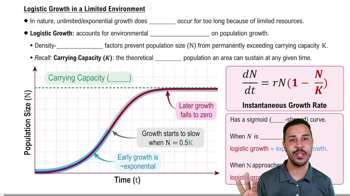
Logistic Population Growth Model
A model that accounts for environmental limitations on population growth, leading to a sigmoidal (S-shaped) curve.
Carrying Capacity (k)
The maximum population size that an environment can sustain indefinitely.
What shape does the logistic growth curve resemble?
An S-shape or sigmoidal curve.
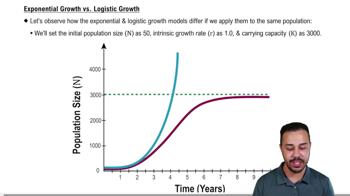
How does the logistic growth model differ from the exponential growth model?
It includes a term for environmental limitations, preventing indefinite growth.
Exponential Growth Model
A population growth model that assumes unlimited resources, leading to continuous and unbounded growth.
What happens to the growth rate as the population size approaches the carrying capacity in the logistic model?
The growth rate slows down and eventually approaches zero.
Instantaneous Growth Rate Equation for Logistic Model
dN/dt = rN(1 - N/K)
What is the initial growth pattern in the logistic model when the population size is small?
It is approximately exponential.
What does the term (1 - N/K) represent in the logistic growth equation?
The environmental limitations on population growth.
What happens if a population temporarily exceeds its carrying capacity?
The population size will decrease or crash shortly after.
Intrinsic Growth Rate (r)
The per capita population growth rate.
What is the carrying capacity's role in the logistic growth model?
It acts as a cap or limit on the population size.
Sigmoidal Curve
A curve that represents logistic growth, shaped like an 'S'.
What is the difference in the r value between exponential and logistic growth models?
In the logistic model, r decreases as population size increases, while it remains constant in the exponential model.
What does the logistic growth model assume about resources?
Resources are limited.
What happens to the population growth rate in the logistic model when N is half of K?
The growth rate starts to slow down.
What is the shape of the exponential growth curve?
A J-shape.
What does the logistic growth model account for that the exponential model does not?
Environmental limitations and carrying capacity.
What is the effect of density dependent factors on population size?
They prevent the population size from permanently exceeding the carrying capacity.
What is the population growth rate when N equals K in the logistic model?
The growth rate is zero.
What is the primary difference between the logistic and exponential growth models?
The logistic model includes a term for environmental limitations.
What does the logistic growth model predict about population size over long periods?
It will stabilize around the carrying capacity.
What is the carrying capacity represented by in equations?
The variable K.
What happens to the population growth rate in the exponential model?
It continuously increases without any limitations.
What is the significance of the term (1 - N/K) in the logistic growth equation?
It adjusts the growth rate based on the population size relative to the carrying capacity.
What is the effect of surpassing the carrying capacity in the logistic model?
The population size will decrease to or below the carrying capacity.
What does the logistic growth model assume about the environment?
It assumes a homogeneous environment and ignores age structure, sex ratio, and external factors.