Back
BackIonic Bonding quiz #1
Terms in this set (15)
What is an ionic bond?
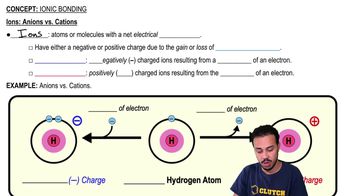
An ionic bond is an electrical attraction between oppositely charged ions, specifically between cations and anions.
How do ionic bonds differ from covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds involve a complete transfer of electrons, whereas covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons.
What happens to the valence shells of atoms involved in ionic bonding?
The complete transfer of electrons fills the valence shells of both atoms involved in the transfer.
Why does sodium transfer an electron to chlorine in the formation of NaCl?
Chlorine is much more electronegative than sodium, causing it to pull on and completely take an electron from sodium.
What charge does a sodium atom acquire after losing an electron?
The sodium atom becomes a positively charged ion (cation) after losing an electron.
What charge does a chlorine atom acquire after gaining an electron?
The chlorine atom becomes a negatively charged ion (anion) after gaining an electron.
What is the result of the attraction between a sodium ion and a chloride ion?
The attraction between a positively charged sodium ion and a negatively charged chloride ion forms an ionic bond.
What common household item is formed by the ionic bonding of sodium and chloride?
Table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), is formed by the ionic bonding of sodium and chloride.
What is the significance of valence shells in ionic bonding?
Filling the valence shells of both atoms involved in ionic bonding stabilizes the atoms and completes their outer electron shells.
How does the concept of electronegativity relate to ionic bonding?
Electronegativity determines how strongly an atom can attract electrons; in ionic bonding, the more electronegative atom takes electrons from the less electronegative atom.
What is the role of electron transfer in the formation of ionic bonds?
Electron transfer creates ions with opposite charges, which then attract each other to form ionic bonds.
What is the relationship between cations and anions in ionic bonding?
Cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions) attract each other to form ionic bonds.
How does ionic bond formation affect the stability of atoms?
Ionic bond formation increases the stability of atoms by filling their valence shells and creating a stable electron configuration.
What is the significance of the complete transfer of electrons in ionic bonding?
The complete transfer of electrons results in the formation of ions with full valence shells, leading to the creation of stable ionic compounds.
How does the formation of NaCl demonstrate the 10% rule in ionic bonding?
The 10% rule is not directly related to ionic bonding; it is more relevant to energy transfer in ecosystems, not the formation of ionic compounds like NaCl.