Introduction to Eukaryotic Gene Regulation exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (26)
Differential gene expression
A process that allows multicellular organisms to express genes differently in different cells, leading to diverse cell types.
What is the role of histone acetylation in gene regulation?
Histone acetylation modifies chromatin structure to make DNA more accessible for transcription.
Chromatin modifications
Changes to the structure of chromatin that affect gene expression, including histone acetylation and DNA methylation.
What is the significance of DNA methylation?
DNA methylation typically represses gene expression by adding methyl groups to DNA, affecting chromatin structure.
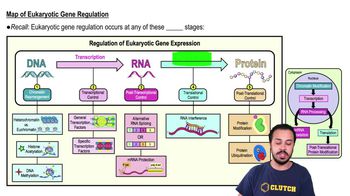
Transcriptional control
Regulation of gene expression at the transcription stage, involving factors that influence the transcription of DNA to RNA.
What is the difference between euchromatin and heterochromatin?
Euchromatin is less condensed and transcriptionally active, while heterochromatin is more condensed and transcriptionally inactive.
Post-translational modifications
Chemical changes to proteins after they are synthesized, affecting their function and activity.
What is RNA interference?
A process where RNA molecules inhibit gene expression by neutralizing targeted mRNA molecules.
Proteome
The entire set of proteins expressed by a cell, tissue, or organism.
What is the function of general transcription factors?
They are essential for the transcription of all genes and help position RNA polymerase at the start of transcription.
Post-transcriptional control
Regulation of gene expression after transcription, including mRNA processing and degradation.
What is protein ubiquitination?
A post-translational modification where ubiquitin proteins are attached to a substrate protein, often marking it for degradation.
Translational control
Regulation of gene expression at the stage of translation, affecting how mRNA is translated into proteins.
What is the role of specific transcription factors?
They regulate the transcription of specific genes by binding to DNA sequences near the genes they control.
Chromatin
A complex of DNA and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
What is mRNA degradation?
The process by which mRNA molecules are broken down, regulating the levels of mRNA available for translation.
Eukaryotic gene regulation
The control of gene expression in eukaryotic cells, occurring at various stages such as chromatin modification, transcription, and translation.
What is the significance of differential gene expression in multicellular organisms?
It allows for the development of diverse cell types despite having identical genomes.
Gene expression
The process by which information from a gene is used to synthesize functional gene products like proteins.
What is the role of chromatin rearrangements in gene regulation?
They alter the structure of chromatin to either promote or inhibit the transcription of genes.
What is the function of the nucleus in gene regulation?
The nucleus is where chromatin modifications, transcription, and RNA processing occur.
What is the role of post-translational control?
It involves modifications to proteins after synthesis, affecting their function and activity.
DNA methylation
The addition of methyl groups to DNA, often serving to repress gene transcription.
What is the relationship between genome and proteome?
The genome is the complete set of DNA, while the proteome is the complete set of proteins expressed by a cell.
Euchromatin
A less condensed form of chromatin that is transcriptionally active.
What is the purpose of mRNA processing?
To modify mRNA after transcription, including splicing, capping, and adding a poly-A tail, to protect and prepare it for translation.