Introduction to Cellular Respiration exam Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to Cellular Respiration exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
- Aerobic Cellular RespirationThe process of breaking down glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce ATP, carbon dioxide, and water.
- What is the main purpose of aerobic cellular respiration?To make lots and lots of ATP or energy for the cell.
- MitochondriaThe organelle where most stages of aerobic cellular respiration occur.
- What does the term 'aerobic' refer to in cellular respiration?The requirement of the presence of oxygen gas (O2).
- GlycolysisThe first stage of aerobic cellular respiration that occurs in the cytoplasm.
- What are the four stages of aerobic cellular respiration?Glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.
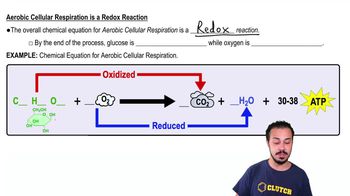
- Redox ReactionA chemical reaction involving the transfer of electrons between molecules.
- What is the chemical formula for glucose?C6H12O6
- Pyruvate OxidationThe second stage of aerobic cellular respiration that occurs in the mitochondria.
- What is the final electron acceptor in aerobic cellular respiration?Oxygen (O2)
- Krebs CycleThe third stage of aerobic cellular respiration, also known as the citric acid cycle.
- What are the byproducts of aerobic cellular respiration?Carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
- Electron Transport ChainThe fourth stage of aerobic cellular respiration where most ATP is produced.
- What mnemonic can help remember the stages of aerobic cellular respiration?Giant Pandas Killed Einstein (Glycolysis, Pyruvate oxidation, Krebs cycle, Electron transport chain).
- Oxidative PhosphorylationThe process of ATP production in the electron transport chain.
- What is the main product of aerobic cellular respiration?ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
- Substrate-Level PhosphorylationA way of generating ATP during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
- What happens to glucose during aerobic cellular respiration?It is oxidized, losing electrons.
- CytoplasmThe location where glycolysis occurs.
- What happens to oxygen during aerobic cellular respiration?It is reduced, gaining electrons.
- ATPThe energy currency of the cell produced during cellular respiration.
- What is the overall chemical equation for aerobic cellular respiration?C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
- ChemiosmosisThe process of ATP generation in the electron transport chain.
- What is the role of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?To produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
- Lactic Acid FermentationA type of anaerobic respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen.
- What are the two types of fermentation?Lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation.
- Anaerobic RespirationCellular respiration that occurs without oxygen, using an alternative final electron acceptor.
- What is the significance of the mitochondria in cellular respiration?It is the site where most stages of aerobic cellular respiration occur.
- Alcohol FermentationA type of anaerobic respiration that produces ethanol and carbon dioxide.