Introduction to Aquatic Biomes exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (29)
Aquatic Biomes
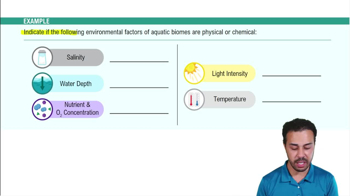
Biomes covered by a significant amount of water, characterized by their physical and chemical environments.
What are the two major categories of aquatic biomes?
Freshwater and marine biomes.
Freshwater Biomes
Biomes with less than 0.1% salt concentration, including lakes, rivers, and streams.
Marine Biomes
Biomes with about 3% salt concentration, including the world's oceans.
What percentage of Earth's water is found in freshwater biomes?
3%
What percentage of Earth's water is found in marine biomes?
97%
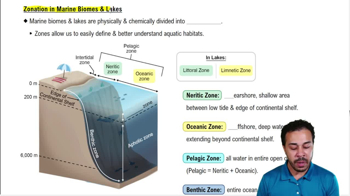
Intertidal Zone
The area between high tide and low tide marks, found only in marine biomes.
Littoral Zone
The near shore shallow area in lakes.
What is the analogous zone to the intertidal zone in lakes?
Lakes do not have an analogous zone to the intertidal zone.
Continental Shelf
The shelf before a major drop-off in marine biomes.
Neuritic Zone
The near shore shallow area between the low tide and the edge of the continental shelf in marine biomes.
Limnetic Zone
The offshore deep water zone in lakes.
Oceanic Zone
The offshore deep water extending beyond the continental shelf in marine biomes.
Pelagic Zone
All the water in the open ocean, combining the neuritic and oceanic zones.
Benthic Zone
The entire bottom of a lake or ocean.
Photic Zone
The surface layer of water that receives enough light for photosynthesis.
Aphotic Zone
The deeper layer of water that does not receive enough light for photosynthesis.
Seasonal Turnover
The vertical mixing of water layers in lakes and oceans during spring and fall.
What drives seasonal turnover?
Changes in water density due to seasonal temperature fluctuations.
Thermocline
A drastic change in temperature over a short distance in water, creating a density gradient.
Ocean Upwelling
The process where deep, cold, nutrient-rich water rises to replace surface waters moving along the coast.
What causes ocean upwelling?
Prevailing winds pushing surface waters along the coast.
Why is ocean upwelling important?
It replenishes surface waters with nutrients and brings oxygen to deeper waters.
What happens to nutrients in lakes and oceans over time?
Nutrients tend to sink towards the bottom, leaving surface waters nutrient-depleted.
What happens to oxygen in lakes and oceans over time?
Oxygen tends to become depleted at the bottom.
What is the maximum density of freshwater?
The maximum density of freshwater occurs at approximately 4°C (39.2°F), where its density is around 1,000 kg/m³ (or 1 g/cm³).
What seasons are most effective for seasonal turnover?
Spring and fall.
What is the primary characteristic that defines aquatic biomes?
Their physical and chemical environments, such as salt concentration.
What is the analogous zone to the oceanic zone in lakes?
The limnetic zone.