Growth exam Flashcards
 Back
BackGrowth exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
- Indeterminate growthGrowth that continues throughout a plant's life.
- What are meristems?Collections of plant stem cells that differentiate into various tissues.
- Primary growthGrowth that extends roots and shoots, occurring at apical meristems.
- Where does secondary growth occur?In woody plants, involving lateral meristems like vascular cambium and cork cambium.
- Vascular cambiumA lateral meristem that produces secondary xylem and phloem.
- What is the function of cork cambium?Forms bark by producing cork cells.
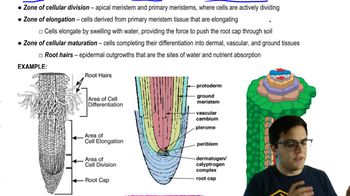
- Root hairsEpidermal outgrowths essential for nutrient absorption.
- What are the three zones of root growth?Zones of cellular division, elongation, and maturation.
- Apical meristemMeristem located at the tip of each root and shoot.
- What does the protoderm give rise to?The epidermis.
- ProcambiumPrimary meristem that gives rise to vascular tissue.
- What is the ground meristem responsible for?Giving rise to ground tissue.
- Zone of cellular divisionArea where cells are actively dividing, found behind the root cap.
- What happens in the zone of elongation?Cells elongate by swelling with water, pushing the root cap through the soil.
- Zone of cellular maturationArea where cells complete their differentiation into various tissue types.
- What is the role of the root cap?Protects the apical meristem and senses gravity.
- Secondary xylemProduced by the vascular cambium, contributing to growth rings.
- What is heartwood?The inner, non-transporting xylem that accumulates gums and resins.
- SapwoodThe outer, actively transporting xylem.
- What forms bark?Cork cells produced by the cork cambium and secondary phloem.
- LenticlesPorous tissues in bark that allow for gas exchange.
- What is the shoot apical meristem?The apical meristem located at the tip of a shoot, giving rise to leaves and flowers.
- Root apical meristemThe apical meristem located at the tip of a root, giving rise to roots.
- What are primary meristems?Meristems that differentiate from apical meristems and are responsible for primary growth.
- Ground tissueTissue that is not vascular or dermal, derived from the ground meristem.
- What is the function of secondary phloem?Produced by the vascular cambium, it contributes to the formation of bark.
- What is the role of the vascular cambium in secondary growth?Produces secondary xylem and phloem, contributing to the plant's circumference.
- Cork cellsNon-living cells produced by the cork cambium, forming bark.
- What is the significance of growth rings in trees?They indicate the age of the tree and are formed by the accumulation of secondary xylem.