Back
BackExperimental Design quiz #1
Terms in this set (27)
What is a false positive in the context of experimental design?
A false positive is an outcome that falsely indicates the presence of a result, such as a pregnancy test indicating pregnancy when the person is not pregnant.
What is a false negative in experimental design?
A false negative is an outcome that falsely indicates the absence of a result, such as a pregnancy test indicating not pregnant when the person is actually pregnant.
Why are control groups important in a well-designed experiment?
Control groups are important because they help prevent false positives and false negatives by providing a baseline for comparison.
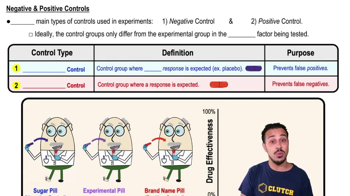
What is the purpose of a negative control in an experiment?
The purpose of a negative control is to prevent false positives by using a group where no response is expected, such as a placebo.
What is the purpose of a positive control in an experiment?
The purpose of a positive control is to prevent false negatives by using a group where a response is expected, such as a proven effective drug.
How does a negative control help in preventing false positives?
A negative control helps prevent false positives by providing a baseline where no response is expected, ensuring that any observed effect is due to the experimental treatment.
How does a positive control help in preventing false negatives?
A positive control helps prevent false negatives by providing a baseline where a response is expected, ensuring that the experimental setup can detect an effect if it exists.
What is the role of the independent variable in an experiment?
The independent variable is the factor that scientists have control over and manipulate to observe its effect on the dependent variable.
What is the role of the dependent variable in an experiment?
The dependent variable is what scientists measure in the experiment, such as drug effectiveness in healing a toe injury.
What would be an example of a negative control in a drug effectiveness experiment?
An example of a negative control would be using a sugar pill (placebo) that is not expected to have any effect on the condition being treated.
What would be an example of a positive control in a drug effectiveness experiment?
An example of a positive control would be using a brand name pill that has been proven to work successfully in the past.
What does it mean if a negative control shows a 100% drug effectiveness?
If a negative control shows 100% drug effectiveness, it indicates a false positive, meaning the placebo had an unexpected effect.
What does it mean if a positive control shows 0% drug effectiveness?
If a positive control shows 0% drug effectiveness, it indicates a false negative, meaning the proven drug did not show the expected effect.
Why is it important to include both positive and negative controls in an experiment?
Including both positive and negative controls is important to ensure the reliability of the experimental results by preventing false positives and false negatives.