Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackEukaryotic Chromatin Modifications quiz
1/16
Terms in this set (16)
- What is histone acetylation?Histone acetylation is the process of adding an acetyl group to histone proteins, which loosens chromatin structure and promotes euchromatin formation.
- How does histone acetylation affect chromatin structure?Histone acetylation loosens the chromatin structure, making DNA more accessible to RNA polymerase and promoting transcription.
- What is the role of histone tails in chromatin modification?Histone tails can be chemically modified by cellular enzymes, such as through acetylation, to regulate chromatin structure and gene expression.
- What happens to chromatin structure during deacetylation?Deacetylation removes acetyl groups from histones, resulting in tighter chromatin packing and a heterochromatin state, which reduces transcription.
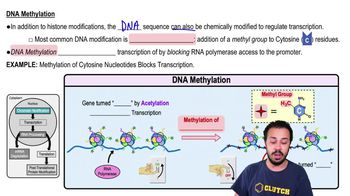
- What is DNA methylation?DNA methylation is the addition of a methyl group to cytosine nucleotides, which typically blocks transcription by preventing RNA polymerase from accessing the promoter.
- How does DNA methylation affect gene expression?DNA methylation turns off gene expression by blocking RNA polymerase from binding to the DNA, thus preventing transcription.
- What is the difference between histone acetylation and DNA methylation?Histone acetylation promotes transcription by loosening chromatin, while DNA methylation inhibits transcription by blocking RNA polymerase access.
- What are transcription factors?Transcription factors are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences to regulate transcription initiation.
- What is the role of general transcription factors?General transcription factors bind to the promoter region and are required for the transcription of all genes.
- How do specific transcription factors differ from general transcription factors?Specific transcription factors bind to regulatory regions other than the promoter and are required for the transcription of specific genes.
- What is the euchromatin state?Euchromatin is a loosely packed chromatin state that allows for active transcription.
- What is the heterochromatin state?Heterochromatin is a tightly packed chromatin state that generally represses transcription.
- What is the function of RNA polymerase in transcription?RNA polymerase binds to DNA and synthesizes RNA during transcription.
- What is the effect of acetylation on gene expression?Acetylation increases gene expression by promoting a euchromatin state, making DNA more accessible for transcription.
- What is the effect of methylation on gene expression?Methylation decreases gene expression by blocking RNA polymerase from accessing the DNA, thus preventing transcription.
- eukaryotic chromatin is composed of which of the following macromolecules?Eukaryotic chromatin is composed of DNA and histone proteins. DNA is wrapped around histone proteins to form nucleosomes, which are the basic units of chromatin.