Endosymbiotic Theory quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (21)
What does the endosymbiotic theory propose about the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts?
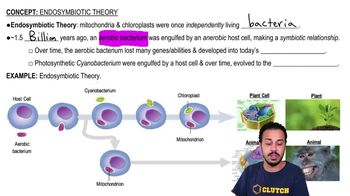
The endosymbiotic theory proposes that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent prokaryotic organisms that were incorporated into eukaryotic cells.
According to the endosymbiotic theory, what type of organism is the ancestor of mitochondria?
The ancestor of mitochondria is believed to be an aerobic prokaryote.
Why can we eliminate eukaryotes as the ancestor of mitochondria in the context of the endosymbiotic theory?
We can eliminate eukaryotes because the endosymbiotic theory specifically states that mitochondria originated from prokaryotic organisms.
Why is cyanobacteria not considered the ancestor of mitochondria?
Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic bacteria, which makes them more likely ancestors of chloroplasts, not mitochondria.
What is the main difference between aerobic and anaerobic bacteria?
Aerobic bacteria require oxygen to function, while anaerobic bacteria do not.
Which type of bacteria is most likely the ancestor of mitochondria according to the endosymbiotic theory?
Aerobic bacteria are most likely the ancestor of mitochondria.
What characteristic of mitochondria supports the idea that they originated from aerobic bacteria?
Mitochondria require oxygen to function, similar to aerobic bacteria.
What is the significance of the endosymbiotic theory in understanding eukaryotic cell evolution?
The endosymbiotic theory helps explain how eukaryotic cells acquired complex organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts through the incorporation of prokaryotic organisms.
How does the endosymbiotic theory relate to the concept of aerobic respiration?
The endosymbiotic theory suggests that mitochondria, which perform aerobic respiration, originated from aerobic bacteria.
What process in mitochondria indicates their prokaryotic origin?
The process of aerobic respiration in mitochondria indicates their prokaryotic origin.
Why is it important to understand the difference between aerobic and anaerobic bacteria in the context of the endosymbiotic theory?
Understanding the difference helps identify the specific type of bacteria that likely became mitochondria, which are aerobic and require oxygen.
What role does oxygen play in the function of mitochondria?
Oxygen is essential for the process of aerobic respiration in mitochondria.
How does the endosymbiotic theory explain the presence of double membranes in mitochondria and chloroplasts?
The double membranes are thought to result from the engulfing of prokaryotic cells by a host eukaryotic cell.
What evidence supports the idea that mitochondria were once free-living prokaryotes?
Mitochondria have their own DNA and ribosomes, similar to prokaryotes, supporting the idea they were once free-living.
How does the endosymbiotic theory contribute to our understanding of cellular respiration?
The theory explains that mitochondria, which are crucial for cellular respiration, originated from aerobic bacteria.
- which statement does not support the endosymbiotic theory?A statement that does not support the endosymbiotic theory would be one that suggests mitochondria and chloroplasts did not originate from independent bacteria or that they do not share similarities with prokaryotes, such as having circular DNA, 70s ribosomes, or replicating via binary fission.
- the endosymbiotic theory helps to explain the origin of which structures?The endosymbiotic theory helps to explain the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells.
- what observation led researchers to propose that chloroplasts evolved from cyanobacteria?Researchers proposed that chloroplasts evolved from cyanobacteria based on observations that chloroplasts and cyanobacteria both perform photosynthesis and share similarities such as circular DNA, 70s ribosomes, and replication via binary fission.
- which of the following statements is true of secondary endosymbiosis?Secondary endosymbiosis involves a eukaryotic cell engulfing another eukaryotic cell that already contains endosymbiotic organelles, such as chloroplasts, leading to complex plastid structures.
- which of the following statements helps support the endosymbiotic theory?Statements that support the endosymbiotic theory include the presence of circular DNA, 70s ribosomes, and binary fission replication in mitochondria and chloroplasts, which are similar to prokaryotic cells.
- which statement is evidence used to support the endosymbiotic theory?Evidence supporting the endosymbiotic theory includes the fact that mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own circular DNA, 70s ribosomes, and replicate independently via binary fission, similar to prokaryotes.