Endosymbiotic Theory definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackEndosymbiotic Theory definitions
1/13
Terms in this set (13)
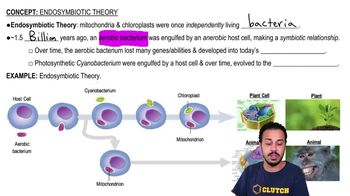
- Endosymbiotic TheoryTheory suggesting mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from free-living prokaryotes that were engulfed by ancestral eukaryotic cells, forming a symbiotic relationship.
- MitochondriaOrganelle in eukaryotic cells, evolved from aerobic bacteria, responsible for producing energy (ATP) through cellular respiration, requiring oxygen to function.
- ChloroplastsPhotosynthetic organelles in eukaryotic cells, believed to have originated from cyanobacteria, responsible for converting light energy into chemical energy via photosynthesis.
- Prokaryotic OrganismsSingle-celled organisms lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, often considered the ancestors of mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells.
- Eukaryotic CellsCells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, believed to have evolved through endosymbiosis, incorporating prokaryotic organisms like mitochondria and chloroplasts.
- ProkaryoteA unicellular organism lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, typically smaller and simpler than eukaryotes, often found in extreme environments.
- EukaryoteAn organism with cells containing a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, believed to have evolved through endosymbiosis of prokaryotic cells.
- CyanobacteriaPhotosynthetic prokaryotes that produce oxygen and are believed to be ancestors of chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells.
- Photosynthetic BacteriaBacteria that perform photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy, and are believed to be ancestors of chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells.
- Aerobic BacteriaBacteria that require oxygen for growth and energy production, often involved in processes like cellular respiration.
- Anaerobic BacteriaBacteria that thrive in environments devoid of oxygen, often using fermentation or anaerobic respiration for energy production.
- Cellular RespirationThe process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy (ATP), carbon dioxide, and water, primarily occurring in the mitochondria.
- OxygenA diatomic molecule essential for aerobic respiration, enabling energy production in mitochondria by acting as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.