Back
BackCommunity Interactions: Competition (-/-) exam
Terms in this set (28)
Competition
When two or more organisms vie for the same limited resource, negatively impacting their fitness.
What is the competitive exclusion principle?
It states that two species with identical niches cannot coexist indefinitely; one will outcompete the other, leading to local extinction.
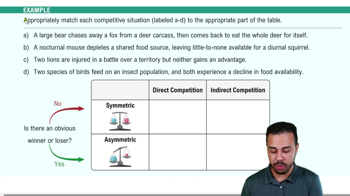
Symmetric competition
Competition where the impact on competing organisms is equal, with no clear winner or loser.
Asymmetric competition
Competition where the impact is unequal, with a clear winner and a clear loser.
What happens to the fitness of organisms in competition?
Both competing organisms experience a decrease in fitness due to the energy and time spent competing.
Niche
A species' ecological role, including its interactions, resource utilization, and the conditions it can tolerate.
What is local extinction?
The exclusion of a species from a particular area or community due to competition.
Resource partitioning
When species with partial niche overlap coexist by utilizing different resources, reducing competition.
Fundamental niche
The full theoretical niche a species could occupy without competition.
Realized niche
The smaller portion of the fundamental niche that a species actually occupies due to competition.
What is character displacement?
The evolution of distinct traits in competing species to minimize competition.
Example of character displacement
The beak depth variation in Galapagos finches to reduce competition for seeds.
Direct competition
When organisms directly interact and compete for the same resource.
Indirect competition
When organisms compete for the same resource without direct interaction.
What is the outcome of complete niche overlap?
Competitive exclusion, where the weaker competitor is driven to local extinction.
Partial niche overlap
When species' niches overlap only partially, allowing for resource partitioning.
What is the impact of competition on growth curves?
Both species show diminished growth when competing, compared to when they grow alone.
Example of resource partitioning
Paramecium species shifting from their fundamental niche to a realized niche to coexist.
What is the significance of character displacement?
It reduces competition, which is favorable for both competing species.
What does competition always result in?
A decrease in fitness for both competing organisms.
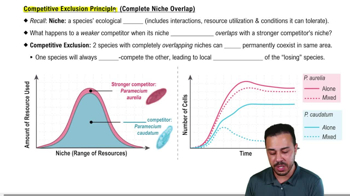
Competitive exclusion principle
Two species with completely overlapping niches cannot coexist indefinitely.
What is the role of energy in competition?
Competing organisms must spend energy and time, reducing their overall fitness.
Local vs Global extinction
Local: species excluded from a specific area. Global: species wiped off the planet.
What allows species to coexist with partial niche overlap?
Resource partitioning, where species utilize different resources.
Impact of competition on weaker competitors
Weaker competitors may shift to a realized niche or face local extinction.
What is the long-term outcome of resource partitioning?
Character displacement, where species evolve distinct traits to reduce competition.
Example of competitive exclusion
Paramecium aurelia outcompeting Paramecium caudatum, leading to the latter's local extinction.
What is the effect of competition on growth curves in mixed cultures?
Both species show diminished growth compared to when they grow alone.