Cancer quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackCancer quiz
1/23
Terms in this set (23)
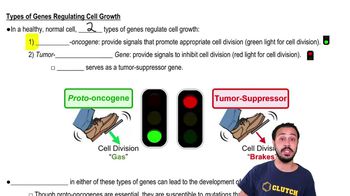
- What are the two types of genes that regulate cell growth in healthy cells?Proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.
- What role do proto-oncogenes play in cell division?Proto-oncogenes act like a green light, promoting appropriate cell division.
- How do tumor suppressor genes affect cell division?Tumor suppressor genes act like a red light, inhibiting and slowing down cell division.
- What is an example of a protein that serves as a tumor suppressor gene?The protein p53.
- What can mutations in proto-oncogenes lead to?Mutations in proto-oncogenes can generate oncogenes, which promote unrestrained cell growth and cancer.
- How do oncogenes differ from proto-oncogenes?Oncogenes are mutated proto-oncogenes that promote unrestrained cell growth.
- What is the primary function of tumor suppressor genes in preventing cancer?They inhibit cell division, preventing uncontrolled cell growth.
- What are alleles?Alleles are alternative or different versions of specific genes.
- How are alleles typically represented in genetics?Alleles are typically represented using capital and lowercase letters.
- What is the difference between a gene and an allele?A gene is a segment of DNA that encodes a specific protein, while an allele is a different version of that gene.
- What can mutations in tumor suppressor genes lead to?Mutations in tumor suppressor genes can lead to the development of cancer.
- What is the role of p53 in cell regulation?p53 is a tumor suppressor protein that helps inhibit cell division.
- What is the relationship between proto-oncogenes and oncogenes?Proto-oncogenes are normal genes that promote cell division, while oncogenes are their mutated forms that cause unrestrained cell growth.
- What is the significance of proto-oncogenes in normal cell function?Proto-oncogenes are essential for promoting appropriate cell division in normal cells.
- How do mutations in proto-oncogenes contribute to cancer?Mutations convert proto-oncogenes into oncogenes, leading to unrestrained cell growth and cancer.
- how has the study of mitosis affected scientists’ knowledge of cancer?The study of mitosis has helped scientists understand that cancer is characterized by uncontrolled cell division. This knowledge has led to the identification of key genes, such as proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, that regulate cell growth and division. Mutations in these genes can lead to cancer development.
- which of the following conditions will most likely cause a normal body cell to become a cancer cell?Mutations in proto-oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes can cause a normal body cell to become a cancer cell by promoting unrestrained cell growth and division.
- what happens when a positive regulator (proto-oncogene) is overactivated?When a proto-oncogene is overactivated, it can become an oncogene, leading to unrestrained cell growth and the development of cancer.
- which of the following describes the normal function of the p53 gene product?The normal function of the p53 gene product is to act as a tumor suppressor, providing signals to inhibit cell division and prevent uncontrolled cell growth.
- which of the following is true concerning cancer cells?Cancer cells are characterized by uncontrolled cell division, the ability to form malignant tumors, and the potential to metastasize to other organs.
- which of the following are ways to differentiate between cancer cells and normal cells?Cancer cells exhibit uncontrolled cell division, form malignant tumors, and can metastasize, whereas normal cells have regulated cell division and do not form malignant tumors or metastasize.
- a child is born with the mutation for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. which of the following is true?The child has a genetic predisposition to developing acute lymphoblastic leukemia due to the inherited mutation, which may affect genes regulating cell growth and division.
- which best describes cancer cells?Cancer cells are characterized by uncontrolled cell division, the formation of malignant tumors, and the ability to metastasize to other parts of the body.