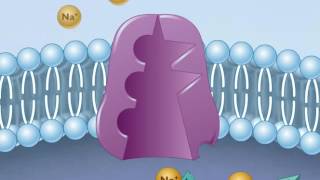
6. The Membrane
Active Transport
6. The Membrane
Active Transport
Showing 5 of 5 videos
Additional 4 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 7 of 7 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
The force driving simple diffusion is ________, while the energy source for active transport is ________.
6379views67rank1comments - Multiple Choice
A sodium-potassium pump ________.
6486views45rank - Multiple Choice
Which of the following defines the type of transport by the sodium-potassium pump?
3889views47rank - Multiple Choice
How are primary and secondary active transport related?
4622views49rank