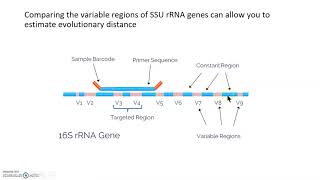
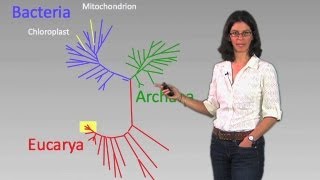
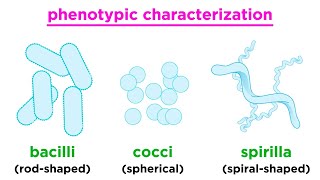
26. Prokaryotes
Prokaryotic Diversity
26. Prokaryotes
Prokaryotic Diversity
Additional 3 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 6 of 6 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following groups of prokaryotes is classified as a member of the domain Archaea?1118views1rank
- Multiple ChoiceWhich subgroup of proteobacteria contains many species that are closely associated with eukaryotic hosts in mutualistic or parasitic relationships?1303views
- Multiple ChoicePortions of the genomes of certain prokaryotic species are very similar to portions of the genomes of distantly related prokaryotes. The process that most likely accounts for this genetic similarity is __________.1347views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich group of bacteria is unusual in that they lack peptidoglycan in their cell walls?1425views