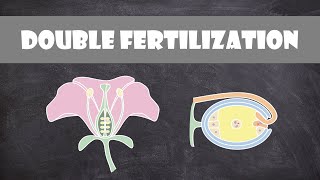
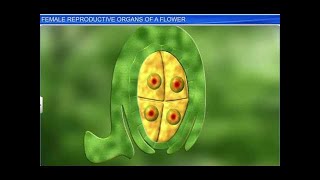
36. Plant Reproduction
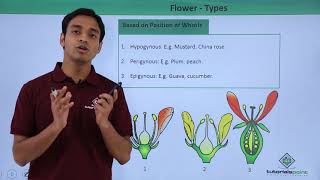
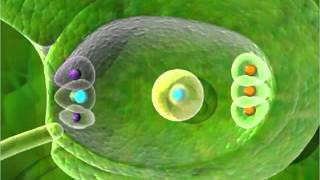
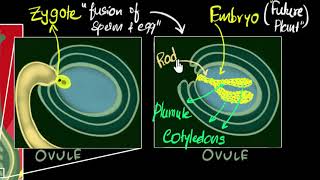
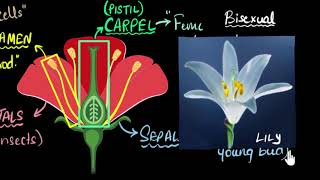
Flowers
36. Plant Reproduction
Flowers
Showing 5 of 5 videos
Additional 25 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 28 of 28 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceThe ABC model of flower formation suggests that __________.1345views
- Multiple ChoiceThe male structures of angiosperms are called __________, and they produce __________.1319views
- Multiple ChoiceIn the alternation of generations in plants, __________.1438views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following associations is correct?1222views