- 1. Introduction to Biology2h 40m
- 2. Chemistry3h 40m
- 3. Water1h 26m
- 4. Biomolecules2h 23m
- 5. Cell Components2h 26m
- 6. The Membrane2h 31m
- 7. Energy and Metabolism2h 0m
- 8. Respiration2h 40m
- 9. Photosynthesis2h 49m
- 10. Cell Signaling59m
- 11. Cell Division2h 47m
- 12. Meiosis2h 0m
- 13. Mendelian Genetics4h 41m
- Introduction to Mendel's Experiments7m
- Genotype vs. Phenotype17m
- Punnett Squares13m
- Mendel's Experiments26m
- Mendel's Laws18m
- Monohybrid Crosses16m
- Test Crosses14m
- Dihybrid Crosses20m
- Punnett Square Probability26m
- Incomplete Dominance vs. Codominance20m
- Epistasis7m
- Non-Mendelian Genetics12m
- Pedigrees6m
- Autosomal Inheritance21m
- Sex-Linked Inheritance43m
- X-Inactivation9m
- 14. DNA Synthesis2h 27m
- 15. Gene Expression3h 20m
- 16. Regulation of Expression3h 31m
- Introduction to Regulation of Gene Expression13m
- Prokaryotic Gene Regulation via Operons27m
- The Lac Operon21m
- Glucose's Impact on Lac Operon25m
- The Trp Operon20m
- Review of the Lac Operon & Trp Operon11m
- Introduction to Eukaryotic Gene Regulation9m
- Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications16m
- Eukaryotic Transcriptional Control22m
- Eukaryotic Post-Transcriptional Regulation28m
- Eukaryotic Post-Translational Regulation13m
- 17. Viruses37m
- 18. Biotechnology2h 58m
- 19. Genomics17m
- 20. Development1h 5m
- 21. Evolution3h 1m
- 22. Evolution of Populations3h 52m
- 23. Speciation1h 37m
- 24. History of Life on Earth2h 6m
- 25. Phylogeny2h 31m
- 26. Prokaryotes4h 59m
- 27. Protists1h 12m
- 28. Plants1h 22m
- 29. Fungi36m
- 30. Overview of Animals34m
- 31. Invertebrates1h 2m
- 32. Vertebrates50m
- 33. Plant Anatomy1h 3m
- 34. Vascular Plant Transport2m
- 35. Soil37m
- 36. Plant Reproduction47m
- 37. Plant Sensation and Response1h 9m
- 38. Animal Form and Function1h 19m
- 39. Digestive System10m
- 40. Circulatory System1h 57m
- 41. Immune System1h 12m
- 42. Osmoregulation and Excretion50m
- 43. Endocrine System4m
- 44. Animal Reproduction2m
- 45. Nervous System55m
- 46. Sensory Systems46m
- 47. Muscle Systems23m
- 48. Ecology3h 11m
- Introduction to Ecology20m
- Biogeography14m
- Earth's Climate Patterns50m
- Introduction to Terrestrial Biomes10m
- Terrestrial Biomes: Near Equator13m
- Terrestrial Biomes: Temperate Regions10m
- Terrestrial Biomes: Northern Regions15m
- Introduction to Aquatic Biomes27m
- Freshwater Aquatic Biomes14m
- Marine Aquatic Biomes13m
- 49. Animal Behavior28m
- 50. Population Ecology3h 41m
- Introduction to Population Ecology28m
- Population Sampling Methods23m
- Life History12m
- Population Demography17m
- Factors Limiting Population Growth14m
- Introduction to Population Growth Models22m
- Linear Population Growth6m
- Exponential Population Growth29m
- Logistic Population Growth32m
- r/K Selection10m
- The Human Population22m
- 51. Community Ecology2h 46m
- Introduction to Community Ecology2m
- Introduction to Community Interactions9m
- Community Interactions: Competition (-/-)38m
- Community Interactions: Exploitation (+/-)23m
- Community Interactions: Mutualism (+/+) & Commensalism (+/0)9m
- Community Structure35m
- Community Dynamics26m
- Geographic Impact on Communities21m
- 52. Ecosystems2h 36m
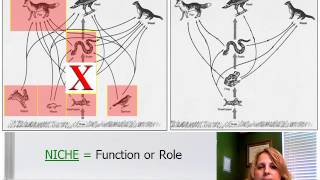
- 53. Conservation Biology24m
53. Conservation Biology
Conservation Biology
Problem 12a
Textbook Question
SCIENTIFIC THINKING The human-generated increase in greenhouse gases (see Module 38.3) provides many opportunities to study the effects of climate change. For example, snowshoe hares are adapted to the climate of their habitat in the taiga of the high mountains and northern regions of North America. One adaptation is seasonal changes in fur color—a white winter coat that turns brown in the spring—that camouflage hares from a long list of predators. These color changes are triggered by day length. As increasing spring temperatures cause earlier snowmelt in the taiga, biologists have observed many white hares sitting on brown earth. Suggest how this natural experiment could be used to investigate the effects of climate change on populations and communities in the taiga ecosystem (assume historical data are available).
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the key variables to study: In this case, the primary variables would be the timing of the snowmelt, the timing of the fur color change in snowshoe hares, and the presence and behavior of predators.
Collect and analyze historical data: Gather historical data on snowmelt timing, hare color change timing, and predator activity in the taiga over several years. This will establish a baseline for normal conditions before significant climate change impacts.
Design a longitudinal study: Set up a study that continuously monitors these variables year over year. This will help in understanding how changes in snowmelt timing due to rising temperatures affect the color change in hares and subsequently their predation rates.
Compare data before and after significant climate change impacts: Analyze the data to see if there are any significant changes in the timing of snowmelt and hare color change, and if these changes correlate with changes in predator behavior and hare population dynamics.
Draw conclusions and predict future impacts: Use the findings to predict how continued climate change will further affect the snowshoe hare populations and the overall taiga ecosystem. Consider factors like genetic adaptation, migration, and changes in predator-prey dynamics.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Climate Change and Ecosystem Dynamics
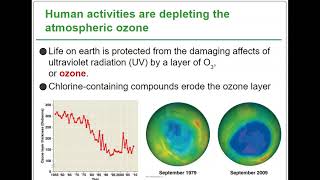
Climate change refers to long-term alterations in temperature and weather patterns, primarily driven by human activities that increase greenhouse gas emissions. These changes can disrupt ecosystems, affecting species interactions, population dynamics, and community structures. Understanding how climate change impacts specific habitats, like the taiga, is crucial for predicting shifts in biodiversity and species survival.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Pollution and Climate Change
Adaptation and Phenotypic Plasticity
Adaptation involves evolutionary changes that enhance a species' survival in its environment, such as the snowshoe hare's seasonal fur color change for camouflage. Phenotypic plasticity refers to the ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to environmental conditions. Studying these adaptations helps biologists understand how species may cope with rapid environmental changes due to climate change.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Phenotypic Plasticity
Natural Experiments and Historical Data
Natural experiments occur when researchers observe real-world scenarios that provide insights into ecological processes without controlled manipulation. Historical data, such as past climate conditions and species distributions, can be invaluable for understanding trends and making predictions about future changes. By analyzing these data alongside current observations, scientists can assess the impacts of climate change on species like the snowshoe hare in the taiga.
Recommended video:
Guided course
The Griffith Experiment

 3:56m
3:56mWatch next
Master Conservation Biology and Biodiversity with a bite sized video explanation from Jason Amores Sumpter
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice