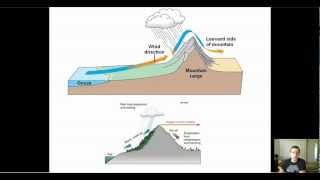
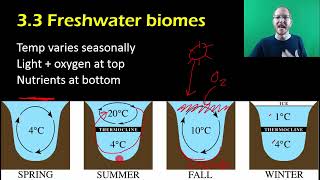
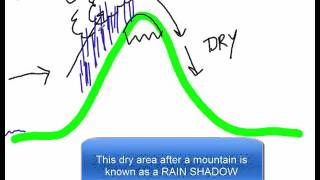
Mountains can have a really interesting effect on climate because they provide a physical barrier in the atmosphere, which is going to impede or at the very least have some effect on airflow. Now, one of the really cool phenomena that can arise from a mountain is what's known as a rain shadow, and this is basically an area that doesn't receive a lot of moisture because it's blocked by a mountain. So what's essentially going to happen is, as warm moist air rises over a mountain, it's going to cool and condense. And when it cools, it's going to lose moisture as precipitation. And so when that air finally gets over the top of the mountain, it's pretty much going to have lost all its moisture. So as it advances and moves over to the other side of the mountain, it's not going to have any moisture to provide as rain. So we are going to have what's called a rain shadow. This dry area is due to a mountain blocking the movement of moist air. Now this can occur on a smaller scale, like we see here, but we actually have a really amazing example on a massive scale, the Himalayas. That's what we're looking at here. These are the Himalayan mountains, sort of on the, you could think of it as the northern edge of the Indian subcontinent, is where you'll find them on a map. And you can see there's a line, literally a line, that goes along here that represents the, essentially the boundary of our rain shadow. Right? It's all green on this side because that's the side that has the moist air. Now, when that air rises over these mountains, it loses its moisture. And that's why this landscape, known as the Tibetan Plateau, is particularly dry because all that rain is being blocked. This is a rain shadow. Now, global air currents will also have a major influence on climate patterns. And you can see that, in this figure we have, what are known as the prevailing winds. These are sort of like major wind patterns, and, you know, of note are these lines in blue, which represent what are called the westerly winds, and because they blow from the West. And then we also have in yellow what are called the trade winds, which are northeasterly winds because they blow from the northeast. Now, there are many other types of global air currents, for example, the jet stream, that are going to have a major influence on the climate patterns around the Earth. It gets very complicated very quickly, and to be honest, people are still sort of understanding some of the science behind it. So, really, all I want you to know about wind is that it can have a global effect, but in local terms, can have a strong effect because wind will actually increase heat loss and water loss. So wind will have a strong effect on local climate and as we can see in this figure, it also will have a major effect on global climate.
So with that, let's go ahead and flip the page.