Multiple Choice
Sucrose has a molecular mass of 342 daltons. To make a 2-molar (2 M) solution of sucrose, __________.
2240
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
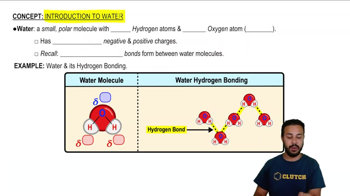

 5:19m
5:19mMaster Properties of Water- The Universal Solvent with a bite sized video explanation from Jason
Start learning