Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chemical Buffers
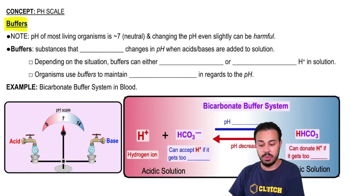
Chemical buffers are solutions that resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added. They typically consist of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. This equilibrium allows buffers to neutralize added acids or bases, maintaining a relatively stable pH in biological and chemical systems.
Recommended video:
pH Scale
The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A pH less than 7 indicates acidity, while a pH greater than 7 indicates basicity. Understanding the pH scale is crucial for comprehending how buffers function, as they are designed to maintain pH levels within a specific range, essential for various biochemical processes.
Recommended video:
Equilibrium Reactions
Equilibrium reactions are chemical reactions that can proceed in both forward and reverse directions, leading to a state where the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. In the context of buffer systems, the equilibrium between a weak acid and its conjugate base allows the system to absorb excess H+ or OH- ions, thus stabilizing the pH. This dynamic balance is key to the effectiveness of buffers in resisting pH changes.
Recommended video:
 Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition Ch. 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance
Ch. 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Problem 18
Problem 18 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance