Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
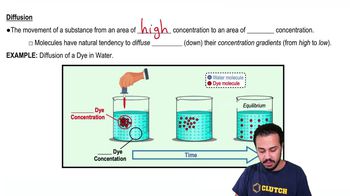
Diffusion
Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This passive transport mechanism is crucial for gas exchange in the lungs, where oxygen diffuses into the blood and carbon dioxide diffuses out, allowing for efficient respiratory function.
Recommended video:
Active Transport
Active transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, requiring energy input, usually in the form of ATP. This process is essential for transporting substances against their concentration gradient, but it is not the primary mechanism for gas exchange in the lungs.
Recommended video:
Cell Membrane Permeability
Cell membrane permeability refers to the ability of substances to pass through the cell membrane. The lipid bilayer of cell membranes allows small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen and carbon dioxide to diffuse freely, facilitating gas exchange in tissues and the lungs without the need for energy.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Membrane Transport
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance