Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Complement System
The complement system is a part of the immune system consisting of proteins that enhance the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear pathogens. It plays a crucial role in the innate and adaptive immune responses, facilitating opsonization, inflammation, and cell lysis. The complement proteins work in a cascade, where the activation of one protein leads to the activation of others, amplifying the immune response.
Recommended video:
Bacterial Lysis
Bacterial lysis refers to the process of breaking down bacterial cells, leading to their destruction. In the context of the complement system, lysis occurs when complement proteins form a membrane attack complex (MAC) that creates pores in the bacterial cell membrane. This disrupts the integrity of the membrane, causing the cell to swell and eventually burst, effectively eliminating the bacterial threat.
Recommended video:
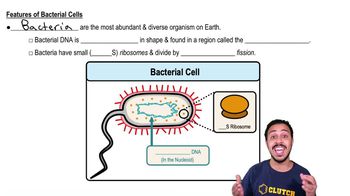
Features of Bacterial Cells
Roles of Complement
Beyond bacterial lysis, the complement system has several other important roles in the immune response. It aids in opsonization, where pathogens are marked for destruction by phagocytes, and promotes inflammation by attracting immune cells to sites of infection. Additionally, complement proteins can enhance the production of antibodies and help clear immune complexes from the bloodstream, contributing to overall immune regulation.
Recommended video:
 Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition Ch. 21 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses
Ch. 21 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Problem 14
Problem 14 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance