Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Interferons
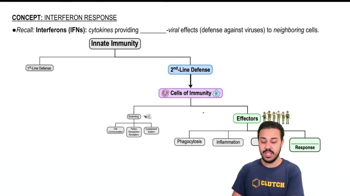
Interferons are a group of signaling proteins produced by host cells in response to viral infections. They play a crucial role in the immune response by enhancing the ability of neighboring cells to resist viral replication. Interferons can also activate immune cells, such as natural killer cells and macrophages, which help eliminate infected cells.
Recommended video:
Stimuli for Interferon Production
The production of interferons is primarily stimulated by the presence of viral pathogens, particularly double-stranded RNA, which is often produced during viral replication. Other stimuli include certain cytokines and the recognition of viral components by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) on host cells. This recognition triggers signaling pathways that lead to the synthesis and release of interferons.
Recommended video:
Cells that Secrete Interferons
Various cells in the body can secrete interferons, with the most notable being virus-infected cells, fibroblasts, and immune cells such as lymphocytes and macrophages. These cells respond to viral infections by producing interferons, which then act on nearby uninfected cells to induce an antiviral state, thereby limiting the spread of the virus.
Recommended video:
 Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn 7th Edition Ch. 21 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses
Ch. 21 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Problem 15
Problem 15 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance