Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary bodily functions, including heart rate and blood pressure. It consists of two main branches: the sympathetic nervous system, which increases heart rate and blood pressure during stress, and the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes relaxation and lowers blood pressure. Understanding the balance between these systems is crucial for comprehending how blood pressure is controlled.
Recommended video:
Somatic vs. Autonomic Nervous System
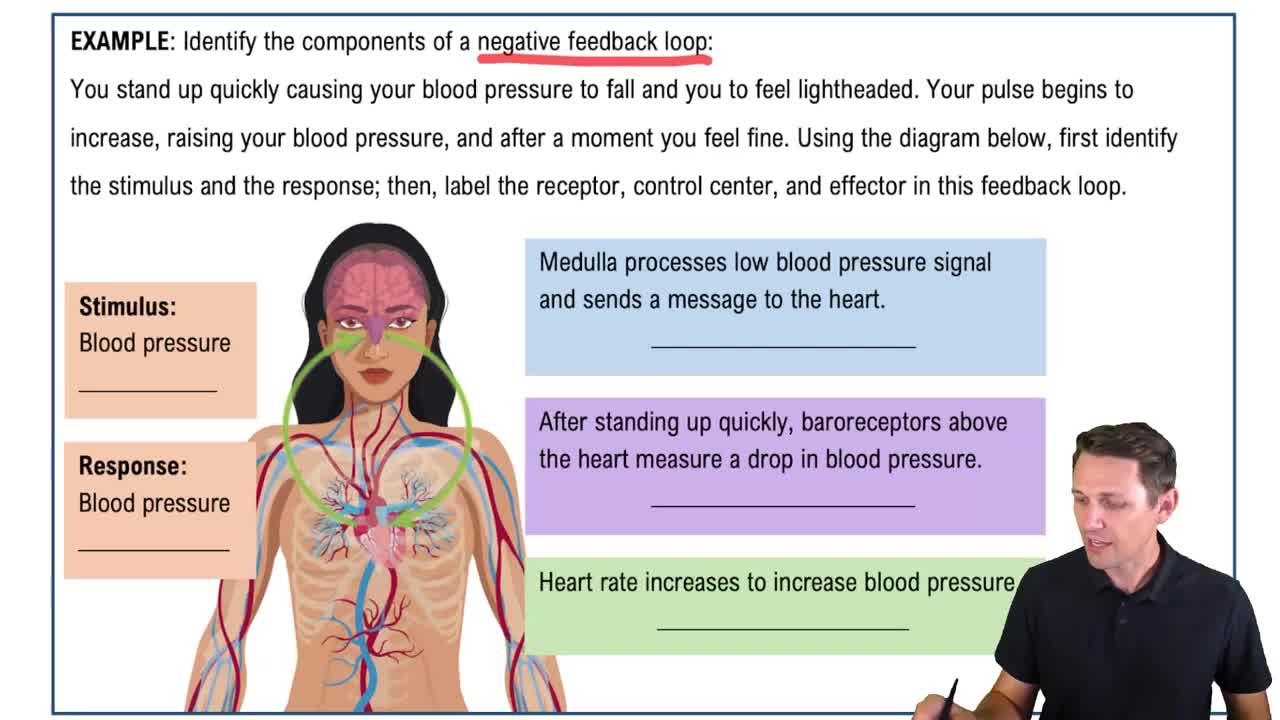
Baroreceptors
Baroreceptors are specialized sensory nerve endings located in the walls of blood vessels, particularly in the carotid arteries and aorta. They detect changes in blood pressure by sensing the stretch of the vessel walls. When blood pressure rises, baroreceptors send signals to the brain to initiate responses that lower blood pressure, illustrating their critical role in maintaining hemodynamic stability.
Recommended video:
Feedback Loops: Negative Feedback Example 1
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure and fluid balance. When blood pressure drops, the kidneys release renin, which leads to the production of angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. This system also stimulates aldosterone release, promoting sodium and water retention, thereby increasing blood volume and pressure. Understanding RAAS is essential for grasping long-term blood pressure regulation.
Recommended video:
External Regulation – Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Mechanism