Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Water
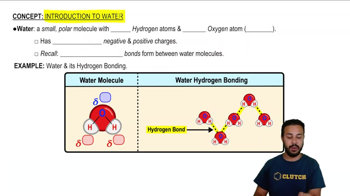
Water is essential for all known forms of life, serving as a solvent for biochemical reactions, a medium for nutrient transport, and a regulator of temperature. It is involved in metabolic processes and is crucial for maintaining cellular structure and function.
Recommended video:
Nutrients
Nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals, are vital for energy production, growth, and cellular repair. They provide the building blocks for biological molecules and are necessary for various physiological functions, including enzyme activity and immune response.
Recommended video:
Gas, Nutrient and Waste Exchange
Oxygen
Oxygen is critical for aerobic respiration, a process through which organisms convert glucose and other substrates into energy. While some life forms can survive without oxygen, most complex organisms rely on it to efficiently produce energy, making it a key factor for sustaining life.
Recommended video:
What Happens to Aerobic Organisms if There's No Oxygen?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance