Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
a. The mass number of an atom is the sum of its neutrons and protons.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

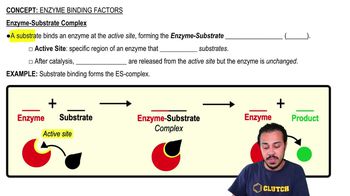
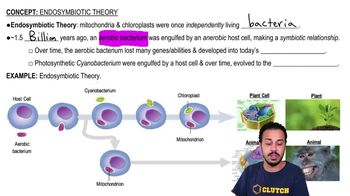
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
a. The mass number of an atom is the sum of its neutrons and protons.
In certain types of radioactive decay, the isotope releases a particle called an alpha particle, which contains two protons and two neutrons. When this happens, is the product still the same element? Why or why not?
The polysaccharide cellulose is not digestible by humans, as we lack the enzyme cellulase, which is required to break it down. Certain dietary supplements contain the enzyme cellulase and claim that being able to break down cellulose will help a person lose weight. But what do you think would happen if we could digest the cellulose we ate?
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
b. Protons and neutrons have a positive charge and electrons have a negative charge.
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
c. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
d. Every element has a characteristic number of protons, which is called the element's mass number.