How does ADH affect the amount of water in the body, and how does it accomplish this? How does this affect the osmolarity of the blood?
What has likely happened to the pH of Mr. Montez's blood? What does this mean about the hydrogen ion concentration in his blood? How will his buffer systems respond to this change in pH?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
pH and Hydrogen Ion Concentration

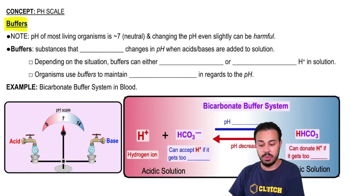
Buffer Systems in Blood
Acidosis and Alkalosis

Mr. Montez is a patient with type I diabetes mellitus. He presents with dizziness, rapid breathing, confusion, and weakness. You find out that he forgot to inject his normal dose of insulin this morning. Will his blood glucose concentration be normal? Explain. Your colleague suggests that Mr. Montez needs to ingest some sugar. Is this going to help him? Why or why not?
Fill in the blanks: Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones are released into the_____system and affect secretion from the_____gland.
List the target tissues and effects of the following anterior pituitary gland hormones.
a. Thyroid-stimulating hormone
b. Adrenocorticotropic hormone
c. Prolactin
d. Gonadotropins
e. Growth hormone
You have read that aldosterone causes sodium ion retention from the kidneys. How would blocking aldosterone secretion decrease the amount of water retained from the fluid in the kidneys?
The thyroid gland consists of:
a. follicle cells that secrete calcitonin.
b. spherical thyroid follicles that contain iodine-containing colloid.
c. parafollicular cells that produce thyroid hormones.
d. spherical thyroid follicles that surround parathyroid hormone–secreting cells.
