Types of Phosphorylation definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTypes of Phosphorylation definitions
1/12
Terms in this set (12)
- Aerobic Cellular RespirationA process that produces ATP using oxygen, involving multiple stages including oxidative phosphorylation.
- ATPA molecule that stores and transfers energy within cells, produced in large amounts during oxidative phosphorylation.
- Substrate-level PhosphorylationA type of phosphorylation that directly generates ATP by transferring a phosphate group to ADP.
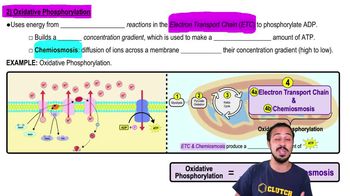
- Oxidative PhosphorylationA process in aerobic respiration that produces ATP using energy from redox reactions in the electron transport chain.
- Electron Transport ChainA series of protein complexes that facilitate redox reactions to create a hydrogen ion gradient for ATP production.
- ChemiosmosisThe movement of hydrogen ions across a membrane, down their gradient, to drive ATP synthesis.
- Redox ReactionsChemical reactions involving the transfer of electrons, crucial for energy generation in the electron transport chain.
- Hydrogen Ion GradientA concentration difference of hydrogen ions across a membrane, used to power ATP synthesis in chemiosmosis.
- ADPA molecule that is phosphorylated to form ATP during oxidative phosphorylation.
- GlycolysisThe first stage of aerobic respiration, breaking down glucose into pyruvate, not directly involved in oxidative phosphorylation.
- Pyruvate OxidationA stage in aerobic respiration converting pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, preceding the Krebs Cycle.
- Krebs CycleA series of reactions generating electron carriers for the electron transport chain, preceding oxidative phosphorylation.