Types of Muscle Tissue definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTypes of Muscle Tissue definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
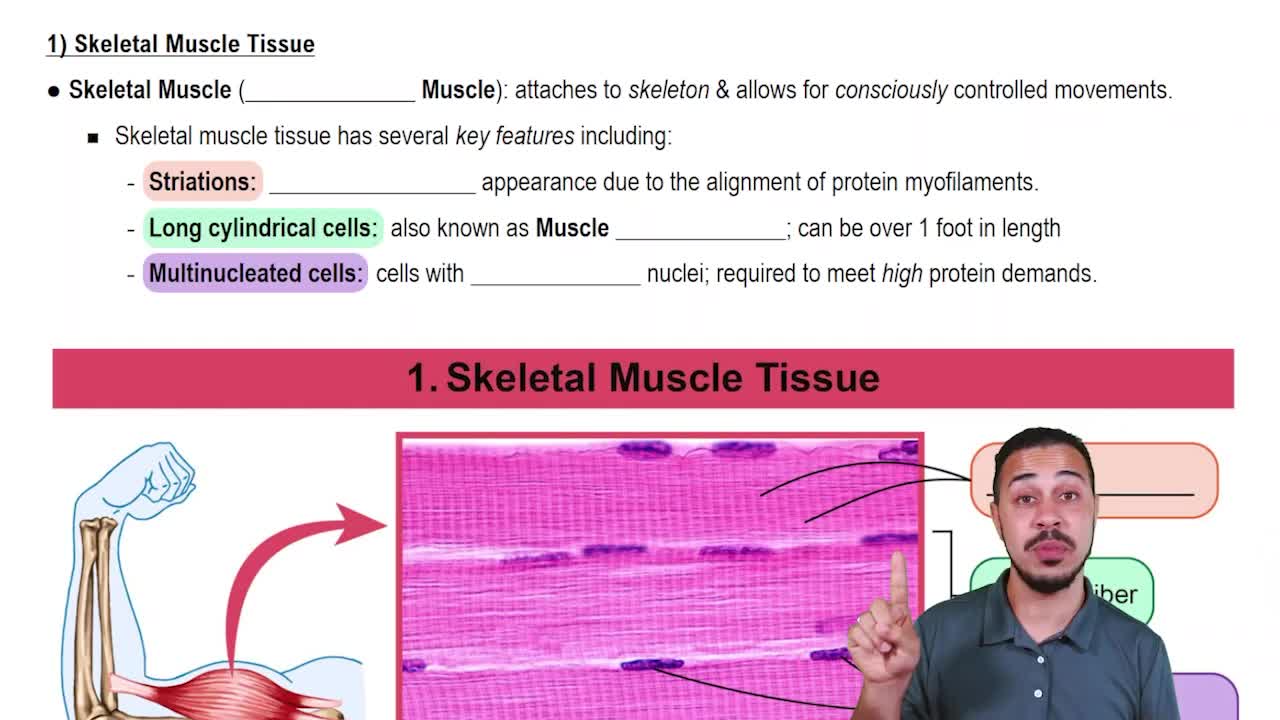
- Skeletal Muscle TissueVoluntary muscle attached to the skeleton, featuring striations and multinucleated, long cylindrical cells.
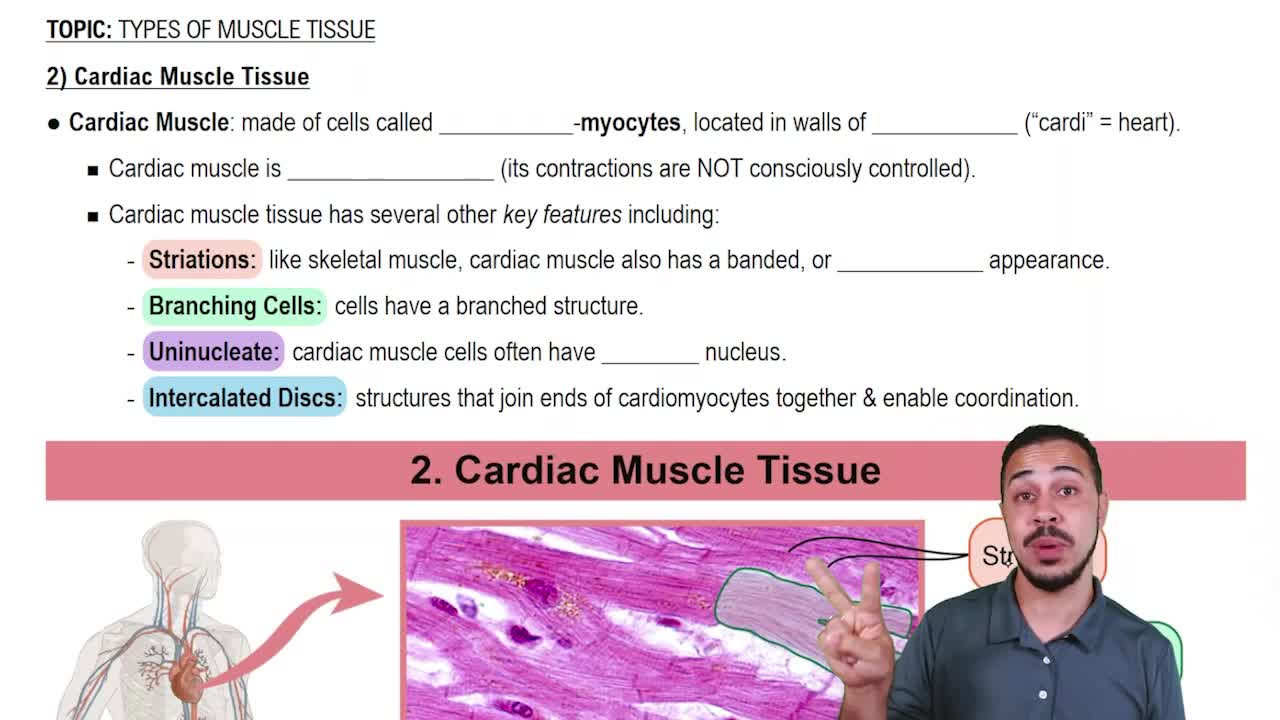
- Cardiac Muscle TissueInvoluntary muscle found in the heart, with striated, branching, uninucleate cells connected by intercalated discs.
- Smooth Muscle TissueInvoluntary muscle in walls of hollow organs, lacking striations, with short, spindle-shaped, uninucleate cells.
- StriationsBanded appearance in muscle tissue due to alignment of protein myofilaments, present in skeletal and cardiac muscles.
- Voluntary MuscleMuscle type under conscious control, allowing for deliberate movements, exemplified by skeletal muscle.
- Involuntary MuscleMuscle type not under conscious control, including cardiac and smooth muscles.
- MultinucleatedCells containing multiple nuclei, characteristic of skeletal muscle fibers to meet high protein demands.
- UninucleateCells with a single nucleus, typical of cardiac and smooth muscle cells.
- CardiomyocytesHeart muscle cells that are striated, branching, and usually uninucleate, forming cardiac muscle tissue.
- Intercalated DiscsStructures connecting cardiomyocytes, enabling coordinated contractions in cardiac muscle tissue.
- Spindle-shaped CellsCells that are narrow at the ends and thicker in the middle, characteristic of smooth muscle tissue.
- Protein MyofilamentsProtein structures in muscle cells responsible for contraction, aligned to form striations in some muscle types.
- TendonsConnective tissues that attach skeletal muscles to bones, facilitating movement.
- BicepsExample of skeletal muscle that can be voluntarily controlled, located in the upper arm.
- Digestive SystemSystem containing smooth muscle tissue in the intestines, aiding in propulsion of food.