Steps of Translation definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackSteps of Translation definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- InitiationThe first step of translation where the ribosome assembles on the mRNA with the start codon AUG.
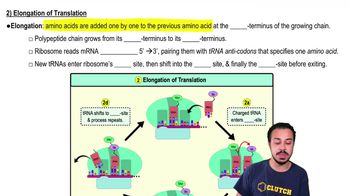
- ElongationThe second step of translation where amino acids are added to the growing polypeptide chain.
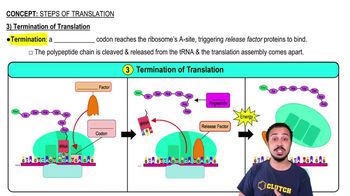
- TerminationThe final step of translation where a stop codon triggers the release of the polypeptide chain.
- RibosomeA molecular machine that facilitates the translation of mRNA into a polypeptide chain.
- mRNAMessenger RNA that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome.
- tRNATransfer RNA that brings amino acids to the ribosome, matching codons with anticodons.
- CodonA sequence of three nucleotides on mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid.
- AnticodonA sequence of three nucleotides on tRNA complementary to a codon on mRNA.
- Start CodonThe codon AUG on mRNA that signals the start of translation and codes for methionine.
- Stop CodonA codon that signals the end of translation, triggering the release of the polypeptide.
- Peptide BondA covalent bond linking amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
- Polypeptide ChainA sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, forming a protein.
- Release FactorA protein that binds to the stop codon, facilitating the release of the polypeptide chain.
- Initiation FactorsProteins that assist in the assembly of the ribosome on the mRNA during initiation.
- Amino AcidThe building block of proteins, specified by codons on mRNA during translation.