Specialized Connective Tissue: Blood definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackSpecialized Connective Tissue: Blood definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
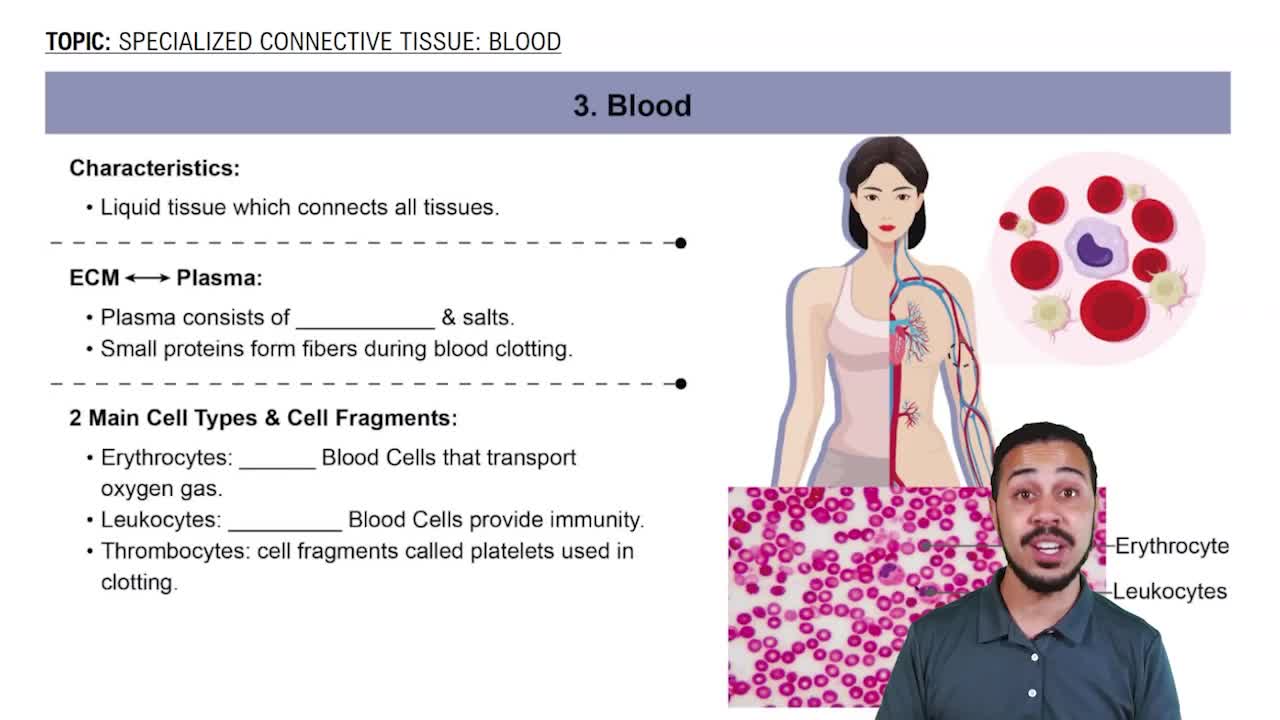
- BloodA liquid connective tissue that transports nutrients and oxygen, connecting all body tissues.
- PlasmaThe extracellular matrix of blood, consisting of water, salts, proteins, and dissolved molecules.
- ErythrocytesRed blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body's tissues.
- LeukocytesWhite blood cells that provide immunity and include various types like macrophages.
- ThrombocytesCell fragments, also known as platelets, crucial for blood clotting to prevent blood loss.
- MacrophageA type of leukocyte that engulfs and eliminates pathogens through phagocytosis.
- Extracellular MatrixThe non-cellular component of blood, known as plasma, lacking fibrous proteins.
- Cardiovascular SystemThe system comprising veins and arteries that transport blood throughout the body.
- Oxygen TransportThe process by which erythrocytes deliver oxygen to tissues across the body.
- ImmunityThe defense mechanism provided by leukocytes to protect the body from pathogens.
- Blood ClottingThe process where plasma proteins form fibers to prevent blood loss.
- PathogensHarmful organisms or substances that leukocytes, like macrophages, target and eliminate.
- PhagocytosisThe process by which macrophages engulf and digest pathogens.
- NutrientsEssential substances transported by blood to support body tissues.
- VeinsBlood vessels that carry blood towards the heart, part of the cardiovascular system.