Secondary Lymphoid Organs: The Spleen definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackSecondary Lymphoid Organs: The Spleen definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
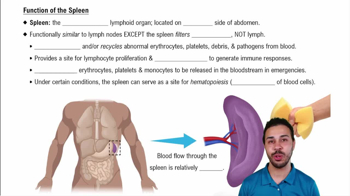
- SpleenLargest lymphoid organ, filters blood, removes old cells, stores blood components, and supports immune function.
- ErythrocytesRed blood cells that are stored and filtered by the spleen, removing old or defective ones.
- White pulpSpleen tissue involved in adaptive immunity, containing T and B lymphocytes.
- Red pulpSpleen tissue involved in innate immunity, filtering blood and removing old erythrocytes.
- MacrophagesCells in the spleen's red pulp that perform phagocytosis, removing abnormal cells.
- Splenic arteryBlood vessel that carries blood into the spleen at the hilum.
- Splenic veinBlood vessel that carries blood out of the spleen at the hilum.
- TrabeculaeInward extensions of the spleen's capsule, providing structural support.
- Venous sinusoidsPermeable capillaries in the spleen's red pulp, allowing passage of normal blood cells.
- HematopoiesisFormation of blood cells, with the spleen as a secondary site under certain conditions.
- Lymphoid folliclesStructures in white pulp containing B lymphocytes, involved in immune response.
- Splenic cordsReticular fiber framework in red pulp, rich in macrophages.
- CapsuleDense irregular connective tissue covering the spleen, providing integrity.
- Central arteriesSmaller branches of the splenic artery around which white pulp is clustered.
- SplenectomySurgical removal of the spleen, affecting immune function and infection risk.