Natural Killer Cells definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackNatural Killer Cells definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
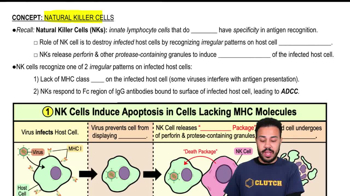
- Natural Killer CellsLymphocytes part of innate immunity, lacking antigen specificity, targeting cells with irregular surface patterns.
- Innate ImmunityThe body's first line of defense, involving non-specific responses to pathogens.
- Adaptive ImmunityImmune response involving specific recognition of antigens, primarily by T cells and B cells.
- LymphocytesWhite blood cells, including NK cells, T cells, and B cells, crucial for immune responses.
- AntigenA molecule capable of inducing an immune response, typically recognized by antibodies or T cells.
- MHC Class IMolecules on cell surfaces presenting antigens to T cells, absence recognized by NK cells.
- ApoptosisProgrammed cell death, a mechanism used by NK cells to eliminate infected cells.
- PerforinA protein released by NK cells creating pores in target cell membranes, aiding in apoptosis.
- ProteaseEnzymes in NK cell granules that degrade proteins, contributing to target cell apoptosis.
- AntibodyProteins produced by B cells that bind to specific antigens, marking them for immune response.
- IgGA type of antibody that can bind to pathogens, facilitating NK cell recognition via the Fc region.
- Fc RegionThe constant region of an antibody, recognized by NK cells during antibody-dependent cytotoxicity.
- Antibody-Dependent Cellular CytotoxicityA process where NK cells induce apoptosis in cells marked by antibodies.
- Cytotoxic GranulesVesicles in NK cells containing perforin and proteases, released to induce apoptosis in target cells.
- Irregular PatternsCell surface anomalies recognized by NK cells, such as absence of MHC class I molecules.