Microscopic Anatomy of Bones - Bone Cells definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackMicroscopic Anatomy of Bones - Bone Cells definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
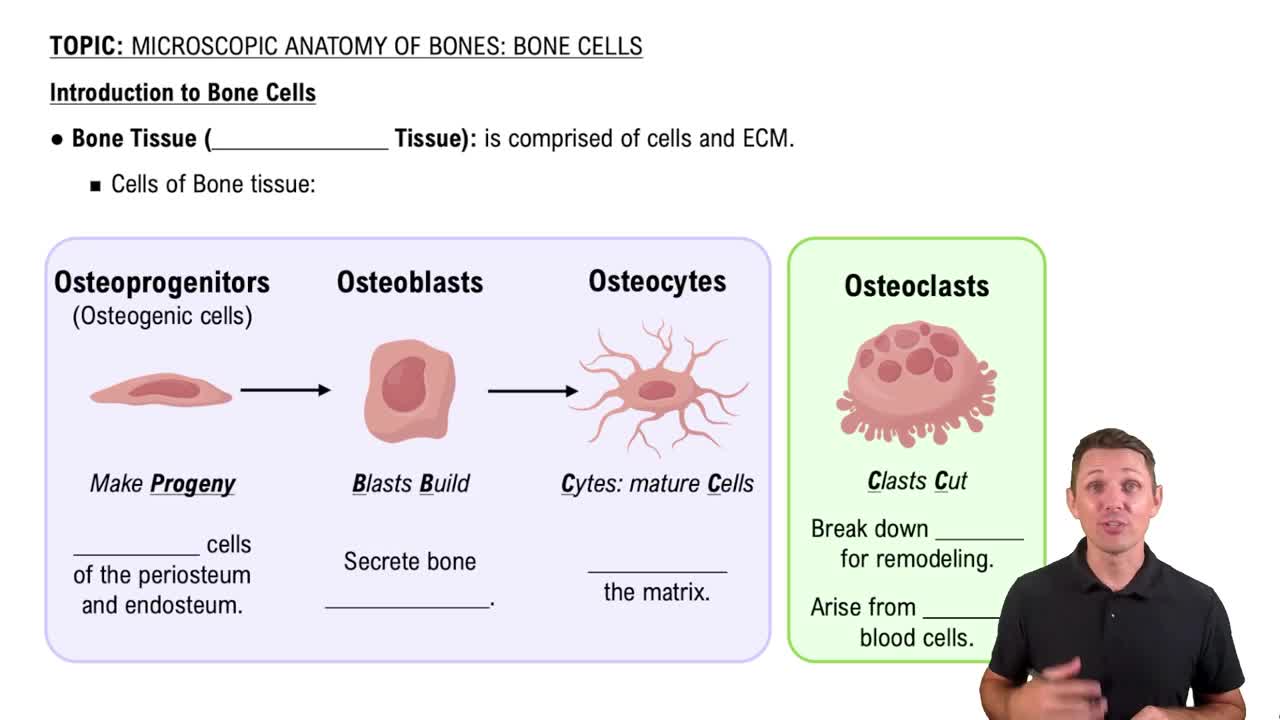
- OsteoprogenitorsBone stem cells in periosteum and endosteum that develop into osteoblasts for bone formation.
- OsteoblastsCells that secrete bone matrix, including collagen and enzymes for hydroxyapatite crystal formation.
- OsteocytesMature bone cells in lacunae that maintain bone matrix and monitor stress.
- OsteoclastsMultinucleated cells that break down bone matrix for remodeling and calcium regulation.
- Extracellular MatrixNon-cellular component of bone tissue, composed of collagen and hydroxyapatite crystals.
- PeriosteumConnective tissue lining the outer surface of bones, containing osteoprogenitor cells.
- EndosteumThin membrane lining the inner surface of bones, housing osteoprogenitor cells.
- LacunaeSmall cavities in bone matrix where osteocytes reside.
- CanaliculiTiny channels in bone matrix allowing nutrient exchange and communication between osteocytes.
- HydroxyapatiteCalcium phosphate crystals providing bone hardness and strength.
- CollagenProtein fibers in bone matrix, providing flexibility and tensile strength.
- Bone RemodelingProcess of bone renewal involving osteoclasts and osteoblasts for maintenance and growth.
- Calcium HomeostasisRegulation of calcium levels in the body, involving bone resorption and formation.
- Ruffled BorderSpecialized structure of osteoclasts increasing surface area for bone resorption.
- OsteolysisProcess of breaking down bone matrix by osteoclasts for resorption.