Introduction to Tissues & Histology definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to Tissues & Histology definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
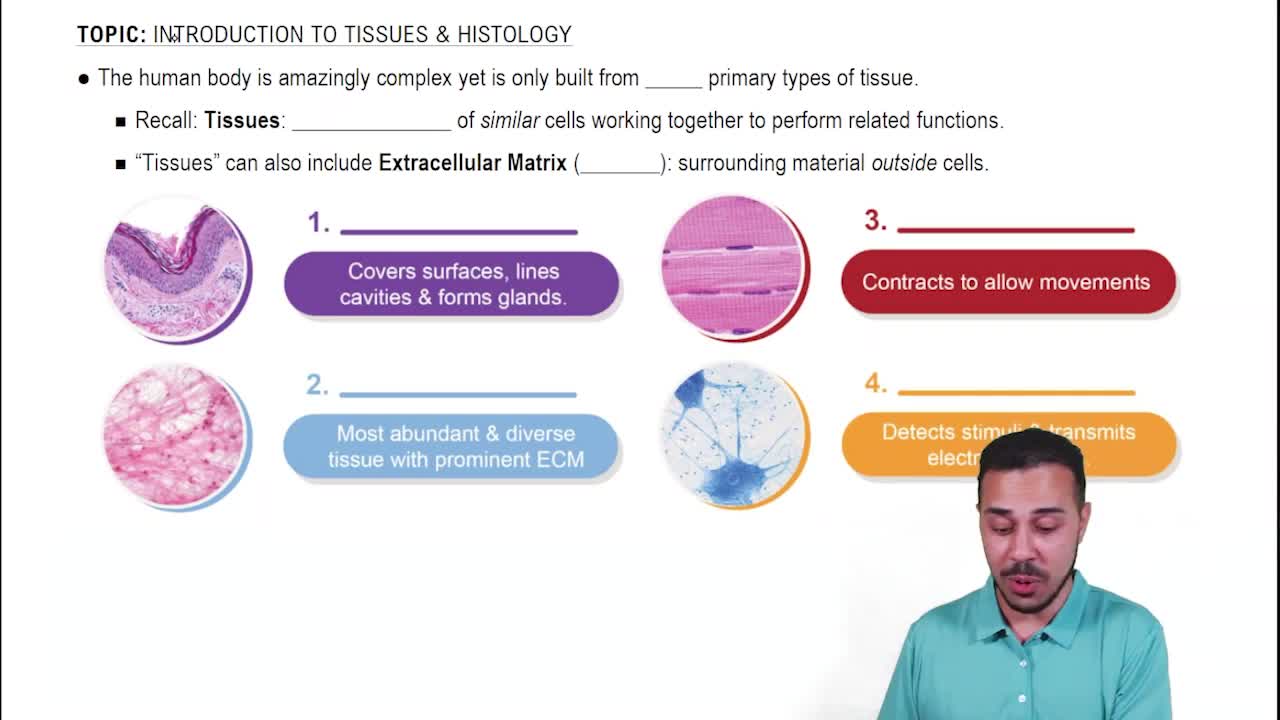
- Epithelial TissueCovers surfaces, lines cavities, and forms glands, with subtypes like covering, lining, and glandular epithelia.
- Connective TissueMost abundant and diverse tissue, with a prominent extracellular matrix, includes cartilage, bones, and blood.
- Muscle TissueResponsible for contraction and body movements, includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle types.
- Nervous TissueDetects stimuli and transmits electrical signals, composed of neurons and neuroglia.
- Extracellular MatrixSurrounding material outside cells, crucial for tissue structure and function, varies in prominence among tissues.
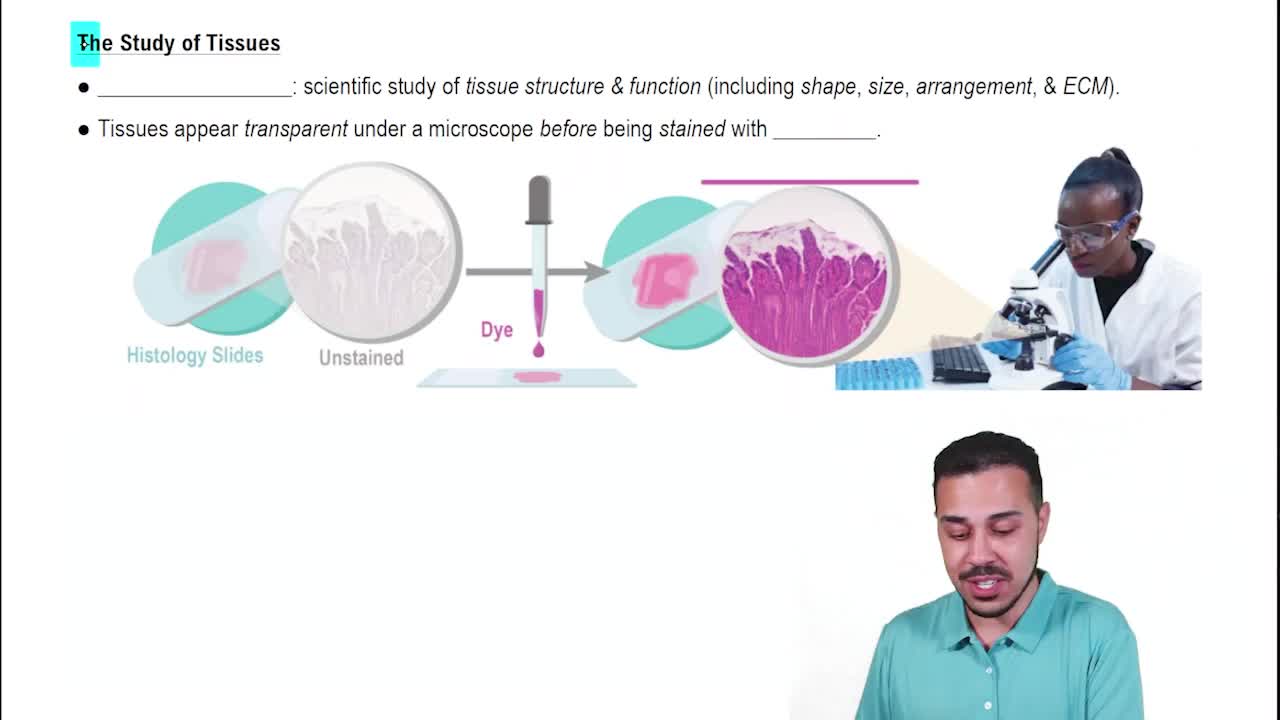
- HistologyScientific study of tissue structure and function, involves microscopy and staining techniques.
- StainingTechnique to enhance tissue visibility under a microscope by adding dyes for better contrast.
- MicrographImage of tissue viewed under a microscope, often stained to improve visualization.
- Glandular EpitheliaType of epithelial tissue involved in secretion, includes exocrine and endocrine glands.
- Connective Tissue ProperIncludes loose and dense connective tissues, with subtypes like areolar, reticular, and adipose.
- CartilageSpecialized connective tissue, includes hyaline, fibrocartilage, and elastic types.
- NeuronsCells in nervous tissue responsible for transmitting electrical signals.
- NeurogliaSupportive cells in nervous tissue that assist neurons.
- MembranesStructures that support and separate body tissues, involved in tissue repair processes.
- Tissue RepairProcess of restoring tissue structure and function after damage.