Introduction to the Lymphatic System definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to the Lymphatic System definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
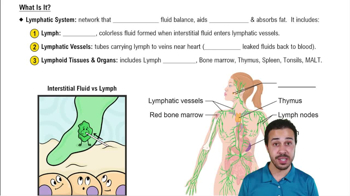
- Lymphatic SystemA network of vessels and organs that maintain fluid balance and aid immunity, addressing cardiovascular system limitations.
- LymphClear fluid formed when interstitial fluid enters lymphatic vessels, differing mainly by location.
- Lymphatic VesselsTube-like structures carrying lymph to veins near the heart, returning leaked fluids and proteins.
- Lymphoid OrgansStructures like lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen involved in immune response and lymphocyte production.
- Interstitial FluidFluid surrounding tissue cells, becoming lymph when entering lymphatic vessels.
- LymphocytesWhite blood cells, including B cells and T cells, crucial for immune response.
- LactealsSpecialized lymphatic capillaries in the small intestine that absorb dietary fats and lipid-soluble vitamins.
- ThymusLymphoid organ where T cells mature, playing a role in immune function.
- SpleenOrgan involved in filtering blood, recycling red blood cells, and housing lymphocytes.
- TonsilsLymphoid tissues located in the throat, involved in trapping pathogens entering through the mouth or nose.
- MALTMucosal associated lymphoid tissues that protect mucosal surfaces from pathogens.
- Bone MarrowPrimary lymphoid organ where blood cells, including lymphocytes, are produced.
- Fluid BalanceMaintenance of fluid levels in the body by returning leaked fluids to the cardiovascular system.
- Immune InteractionsProcesses involving lymphocytes and pathogens, optimized by the lymphatic system.
- MacromoleculesLarge molecules like fats, absorbed by the lymphatic system, not effectively by the cardiovascular system.