Introduction to Cells of the Immune System definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to Cells of the Immune System definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
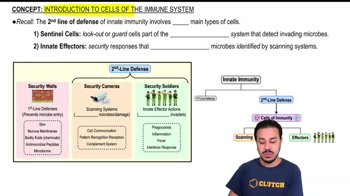
- Sentinel cellsGuard cells in the immune system that detect invading microbes using censoring systems.
- Innate effectorsCells that eliminate identified microbes, acting as security soldiers in the immune response.
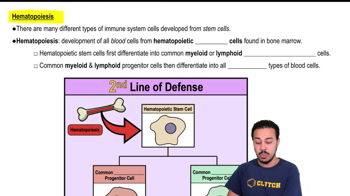
- HematopoiesisThe process of developing blood cells from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow.
- Hematopoietic stem cellsCells in the bone marrow that differentiate into common myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells.
- Common myeloid progenitorA cell type derived from hematopoietic stem cells that differentiates into various blood cells.
- Common lymphoid progenitorA cell type derived from hematopoietic stem cells that differentiates into lymphocytes.
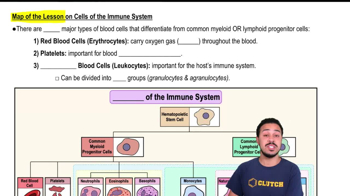
- ErythrocytesRed blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body.
- PlateletsCell fragments important for blood clotting, derived from myeloid progenitor cells.
- LeukocytesWhite blood cells crucial for the immune system, divided into granulocytes and agranulocytes.
- GranulocytesA group of leukocytes including neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils.
- AgranulocytesA group of leukocytes including lymphocytes such as T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells.
- Natural killer cellsLymphocytes part of innate immunity, responsible for destroying infected or cancerous cells.
- T cellsLymphocytes part of adaptive immunity, involved in cell-mediated immune responses.
- B cellsLymphocytes part of adaptive immunity, responsible for producing antibodies.
- Pattern recognition receptorsMolecules on sentinel cells that detect microbial components and initiate immune responses.