Identifying Types of Epithelial Tissue definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIdentifying Types of Epithelial Tissue definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- MicrographAn image of a tissue sample taken through a microscope, used for identifying cellular structures.
- Epithelial TissueA type of tissue composed of one or more layers of tightly packed cells forming a boundary adjacent to open space.
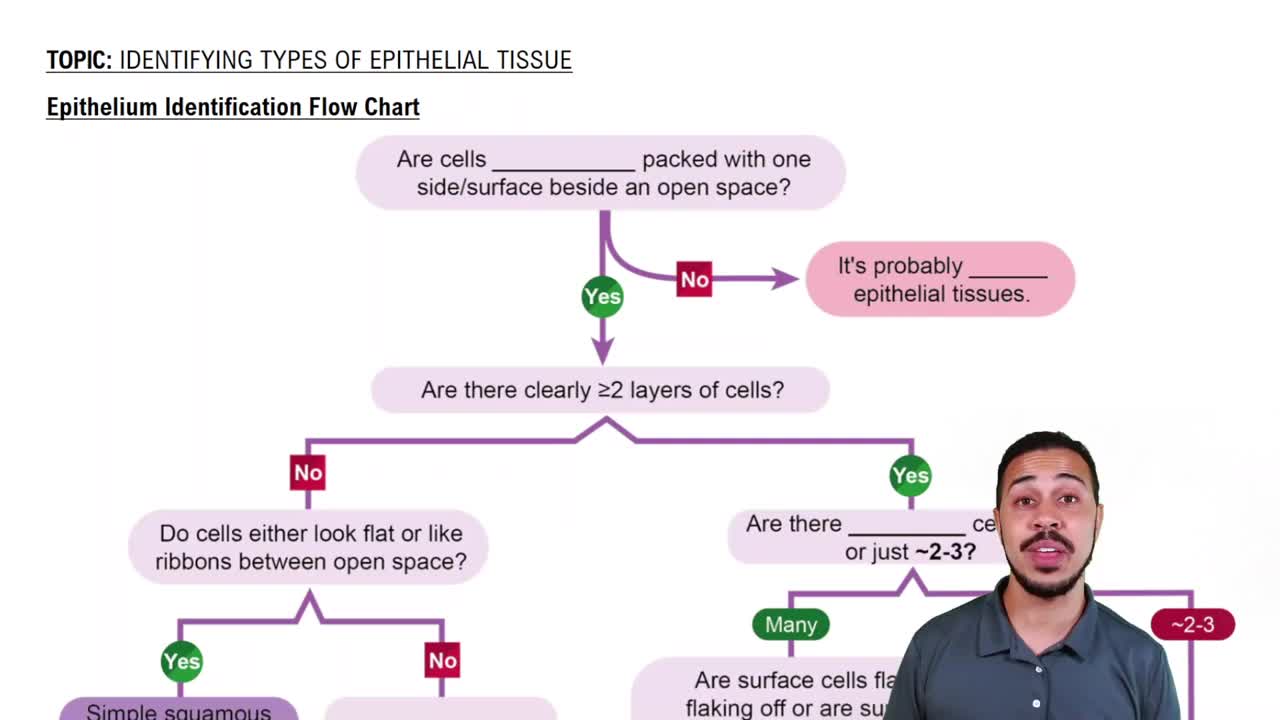
- FlowchartA diagrammatic representation used to identify types of epithelial tissue based on specific characteristics.
- Simple EpitheliumA single layer of epithelial cells, allowing for processes like diffusion and absorption.
- Stratified EpitheliumMultiple layers of epithelial cells, providing protection in areas subject to abrasion.
- SquamousFlat, thin cells that facilitate rapid diffusion, often found in the air sacs of lungs.
- CuboidalCube-shaped cells, often forming ducts and tubules, providing secretion and absorption functions.
- ColumnarTall, narrow cells, often with microvilli or cilia, found lining the digestive and respiratory tracts.
- PseudostratifiedAppears stratified due to nuclei at different levels, but all cells contact the basement membrane.
- Transitional EpitheliumElastic tissue that transitions from cuboidal to squamous shape, lining the urinary bladder.
- KeratinizedA form of stratified squamous epithelium containing keratin, found in the skin.
- Non-keratinizedStratified squamous epithelium without keratin, found in moist areas like the oral cavity.
- CiliaHair-like structures on columnar cells that move substances across the epithelial surface.
- MicrovilliSmall projections on columnar cells that increase surface area for absorption.
- Goblet CellsCells that secrete mucus, found in columnar and pseudostratified epithelia.